Home > Press > A KAIST research team has developed a fully functional flexible memory
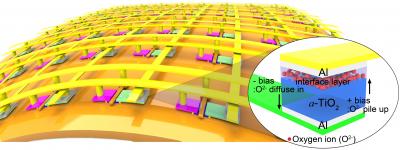 |
| This is a schematic of a fully functional flexible memory array on flexible substrates.
Credit: KAIST |
Abstract:
The team of Professor Keon Jae Lee (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST) has developed fully functional flexible non-volatile resistive random access memory (RRAM) where a memory cell can be randomly accessed, written, and erased on a plastic substrate.
A KAIST research team has developed a fully functional flexible memory
South Korea | Posted on November 5th, 2011Memory is an essential part in electronic systems, as it is used for data processing, information storage and communication with external devices. Therefore, the development of flexible memory has been a challenge to the realization of flexible electronics.
Although several flexible memory materials have been reported, these devices could not overcome cell-to-cell interference due to their structural and material limitations. In order to solve this problem, switching elements such as transistors must be integrated with the memory elements. Unfortunately, most transistors built on plastic substrates (e.g., organic/oxide transistors) are not capable of achieving the sufficient performance level with which to drive conventional memory. For this reason, random access memory operation on a flexible substrate has not been realized thus far.
Recently, Prof. Lee's research team developed a fully functional flexible memory that is not affected by cell-to-cell interference. They solved the cell-to-cell interference issue by integrating a memristor (a recently spotlighted memory material as next-generation memory elements) with a high-performance single-crystal silicon transistor on flexible substrates. Utilizing these two advanced technologies, they successfully demonstrated that all memory functions in a matrix memory array (writing/reading/erasing) worked perfectly.
Prof. Lee said, "This result represents an exciting technology with the strong potential to realize all flexible electronic systems for the development of a freely bendable and attachable computer in the near future."
This result was published in the October online issue of the Nano Letters ACS journal.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lan Yoon
82-423-502-295
Copyright © The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








