Home > Press > NIST Prototype 'Optics Table on a Chip' Places Microwave Photon in Two Colors at Once
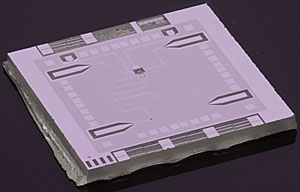 |
| NIST's "optics table on a chip" is a superconducting circuit on a square sapphire chip about 6 millimeters wide. Scientists use the chip to place a single microwave photon in two frequencies, or colors, at the same time. The photon is prepared by an "artificial atom" (small yellow square) in the middle of the chip. The arrow shape at the lower left connects to a transmission line used to tune the SQUID (small black area near the point of the arrow). The SQUID couples together two resonant frequencies of the cavity (meandering line), and the photon oscillates between different superpositions of those frequencies. Credit: D. Schmidt/NIST |
Abstract:
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have created a tunable superconducting circuit on a chip that can place a single microwave photon (particle of light) in two frequencies, or colors, at the same time.
NIST Prototype 'Optics Table on a Chip' Places Microwave Photon in Two Colors at Once
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on July 7th, 2011This curious "superposition," a hallmark of the quantum world, is a chip-scale, microwave version of a common optics experiment in which a device called a beam-splitter sends a photon into either of two possible paths across a table of lasers, lenses and mirrors. The new NIST circuit can be used to create and manipulate different quantum states, and is thus a prototype of the scientific community's long-sought "optics table on a chip."
Described in Nature Physics,* the NIST experiments also created the first microwave-based bit for linear optical quantum computing. This type of quantum computer is typically envisioned as storing information in either the path of a light beam or the polarization (orientation) of single photons. In contrast, a microwave version would store information in a photon's frequency. Quantum computers, if they can be built, could solve certain problems that are intractable today.
The new NIST circuit combines components used in superconducting quantum computing experiments—a single photon source, a cavity that naturally resonates or vibrates at particular frequencies, and a coupling device called a SQUID (superconducting quantum interference device). Scientists tuned the SQUID properties to couple together two resonant frequencies of the cavity and then manipulated a photon to make it oscillate between different superpositions of the two frequencies. For instance, the photon could switch back and forth from equal 50/50 proportions of both frequencies to an uneven 75/25 split. This experimental setup traps photons in a "box" (the cavity) instead of sending them flying across an optical table.
"This is a new way to manipulate microwave quantum states trapped in a box," says NIST physicist José Aumentado, a co-author of the new paper. "The reason this is exciting is it's already technically feasible to produce interesting quantum states in chip-scale devices such as superconducting resonators, and now we can manipulate these states just as in traditional optics setups."
NIST researchers can control how the new circuit couples different quantum states of the resonator over time. As a result, they can create sequences of interactions to make simple optical circuits and reproduce traditional optics experiments. For example, they can make a measurement tool called an interferometer based on the frequency/color of a single photon, or produce special quantum states of light such as "squeezed" light.
* E. Zakka-Bajjani, F. Nguyen, M. Lee, L.R. Vale, R.W. Simmonds and J. Aumentado. Quantum superposition of a single microwave photon in two different 'colour' states. Nature Physics. Posted online July 3, 2011.
####
About NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Ost
303-497-4880
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Lab-on-a-chip
![]() Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
![]() Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








