Home > Press > Penn Physicists Observe “Campfire Effect” in Blinking Nanorod Semiconductors
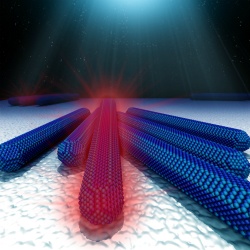 |
| As more nanorods are added to a cluster, the cluster's "on" time dramatically increases. (Art: Robert Johnson) |
Abstract:
When semiconductor nanorods are exposed to light, they blink in a seemingly random pattern. By clustering nanorods together, physicists at the University of Pennsylvania have shown that their combined "on" time is increased dramatically providing new insight into this mysterious blinking behavior.
Penn Physicists Observe “Campfire Effect” in Blinking Nanorod Semiconductors
Philadelphia, PA | Posted on June 23rd, 2011The research was conducted by associate professor Marija Drndic's group, including graduate student Siying Wang and postdoctorial fellows Claudia Querner and Tali Dadosh, all of the Department of Physics and Astronomy in Penn's School of Arts and Sciences. They collaborated with Catherine Crouch of Swarthmore College and Dmitry Novikov of New York University's School of Medicine.
Their research was published in the journal Nature Communications.
When provided with energy, whether in the form of light, electricity or certain chemicals, many semiconductors emit light. This principle is at work in light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, which are found in any number of consumer electronics.
At the macro scale, this electroluminescence is consistent; LED light bulbs, for example, can shine for years with a fraction of the energy used by even compact-fluorescent bulbs. But when semiconductors are shrunk down to nanometer size, instead of shining steadily, they turn "on" and "off" in an unpredictable fashion, switching between emitting light and being dark for variable lengths of time. For the decade since this was observed, many research groups around the world have sought to uncover the mechanism of this phenomenon, which is still not completely understood.
"Blinking has been studied in many different nanoscale materials for over a decade, as it is surprising and intriguing, but it's the statistics of the blinking that are so unusual," Drndic said. "These nanorods can be ‘on' and ‘off' for all scales of time, from a microsecond to hours. That's why we worked with Dmitry Novikov, who studies stochastic phenomena in physical and biological systems. These unusual Levi statistics arise when many factors compete with each other at different time scales, resulting in a rather complex behavior, with examples ranging from earthquakes to biological processes to stock market fluctuations."
Drndic and her research team, through a combination of imaging techniques, have shown that clustering these nanorod semiconductors greatly increases their total "on" time in a kind of "campfire effect." Adding a rod to the cluster has a multiplying effect on the "on" period of the group.
"If you put nanorods together, if each one blinks in rare short bursts, you would think the maximum ‘on' time for the group will not be much bigger than that for one nanorod, since their bursts mostly don't overlap," Novikov said. "What we see are greatly prolonged ‘on' bursts when nanorods are very close together, as if they help each other to keep shining, or ‘burning.'"
Drndic's group demonstrated this by depositing cadmium selenide nanorods onto a substrate, shining a blue laser on them, then taking video under an optical microscope to observe the red light the nanorods then emitted. While that technique provided data on how long each cluster was "on," the team needed to use transmission electron microscopy, or TEM, to distinguish each individual, 5-nanometer rod and measure the size of each cluster.
A set of gold gridlines allowed the researchers to label and locate individual nanorod clusters. Wang then accurately overlaid about a thousand stitched-together TEM images with the luminescence data that she took with the optical microscope. The researchers observed the "campfire effect" in clusters as small as two and as large as 110, when the cluster effectively took on macroscale properties and stopped blinking entirely.
While the exact mechanism that causes this prolonged luminescence can't yet be pinpointed, Drndic's team's findings support the idea that interactions between electrons in the cluster are at the root of the effect.
"By moving from one end of a nanorod to the other, or otherwise changing position, we hypothesize that electrons in one rod can influence those in neighboring rods in ways that enhance the other rods' ability to give off light," Crouch said. "We hope our findings will give insight into these nanoscale interactions, as well as helping guide future work to understand blinking in single nanoparticles."
As nanorods can be an order of magnitude smaller than a cell, but can emit a signal that can be relatively easily seen under a microscope, they have been long considered as potential biomarkers. Their inconsistent pattern of illumination, however, has limited their usefulness.
"Biologists use semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent labels. One significant disadvantage is that they blink," Drndic said. "If the emission time could be extended to many minutes it makes them much more usable. With further development of the synthesis, perhaps clusters could be designed as improved labels."
Future research will use more ordered nanorod assemblies and controlled inter-particle separations to further study the details of particle interactions.
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Office of University Communications
200 Sansom Place East, 3600 Chestnut Street
Philadelphia, PA 19104-6106
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Their research was published in the journal Nature Communications.
Their research was published in the journal Nature Communications.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








