Home > Press > Researchers find replacement for rare material indium tin oxide
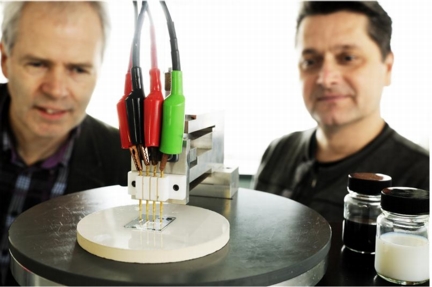 |
| 4-point conductivity measurement of the new transparent conducting film developed by prof. Cor Koning (left) and prof. Paul van der Schoot (right). The black pot contains a dispersion of carbon nanotubes in water, and the white pot contains the conducting latex. Photo: Bart van Overbeeke. |
Abstract:
Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e, Netherlands) have developed a replacement for indium tin oxide (ITO), an important material used in displays for all kinds of everyday products such as TVs, telephones and laptops, as well as in solar cells. Unfortunately indium is a rare metal, and the available supplies are expected to be virtually exhausted within as little as ten years. The replacement material is a transparent, conducting film produced in water, and based on electrically conducting carbon nanotubes and plastic nanoparticles. It is made of commonly available materials, and on top of that is also environment-friendly. The results, which also provide new insights into conduction in complex composite materials, were published online yesterday 10 April by the scientific journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Researchers find replacement for rare material indium tin oxide
Eidhoven, The Netherlands | Posted on April 11th, 2011The research team has been able to achieve higher conductivity by combining low concentrations of carbon nanotubes and conducting latex in a low-cost polystyrene film. The nanotubes and the latex together account for less than 1 percent of the weight of the conducting film. That is important, because a high concentration of carbon nanotubes makes the film black and opaque, so the concentration needs to be kept as low as possible. The research team was led by theoretical physicist Paul van der Schoot and polymer chemist Cor Koning. Post-doc Andriy Kyrylyuk is the first author of the paper in Nature Nanotechnology.
The researchers use standard, widely available nanotubes which they dissolve in water. Then they add conducting latex (a solution of polymer beads in water), together with a binder in the form of polystyrene beads. When the mixture is heated, the polystyrene beads fuse together to form the film, which contains a conducting network of nanotubes and beads from the conducting latex. The water, which only serves as a dispersing agent in production, is removed by freeze-drying. The ‘formula' is not a question of good luck, as the researchers first calculated the expected effects and also understand how the increased conductivity works.
The conductivity of the transparent e film is still a factor 100 lower than that of indium tin oxide. But Van der Schoot and Koning expect that the gap can quickly be closed. "We used standard carbon nanotubes, a mixture of metallic conducting and semiconducting tubes", says Cor Koning. "But as soon as you start to use 100 percent metallic tubes, the conductivity increases greatly. The production technology for 100 percent metallic tubes has just been developed, and we expect the price to fall rapidly." However the conductivity of the film is already good enough to be used immediately as an antistatic layer for displays, or for EMI shielding to protect devices and their surroundings against electromagnetic radiation.
The film has an important advantage over ITO: it is environment-friendly. All the materials are water based, and no heavy metals such as tin are used. The new film is also a good material for flexible displays.
The researchers themselves are very positive about the diversity of their team, which they believe made an important contribution to the results. "We had a unique combination of theoreticians, modeling specialists and people to do practical experiments", says Paul van der Schoot. "Without that combination we wouldn't have succeeded."
The article ‘'Controlling Electrical Percolation in Multi-Component Carbon Nanotube Dispersions' was published yesterday, Sunday 10 april, on the website of the journal Nature Nanotechnology (DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.40). The research forms part of the Functional Polymer Systems research program at the Dutch Polymer Institute (DPI), which provided financial support for this project. Prof. Cor Koning is with the Polymer Chemistry group (Department of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry) and prof. Paul van der Schoot is with the Theory of Polymers and Soft Matter group (Department of Applied Physics) of Eindhoven University of Technology. The other authors of the article are Andriy Kyrylyuk (first author), Marie Claire Hermant, Tanja Schilling and Bert Klumperman.
Andriy Kyrylyuk is the first author of the paper in Nature Nanotechnology. DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.40
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ivo Jongsma
+31 40 247 2110
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








