Home > Press > RNA-Exporting Machine Deciphered at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source
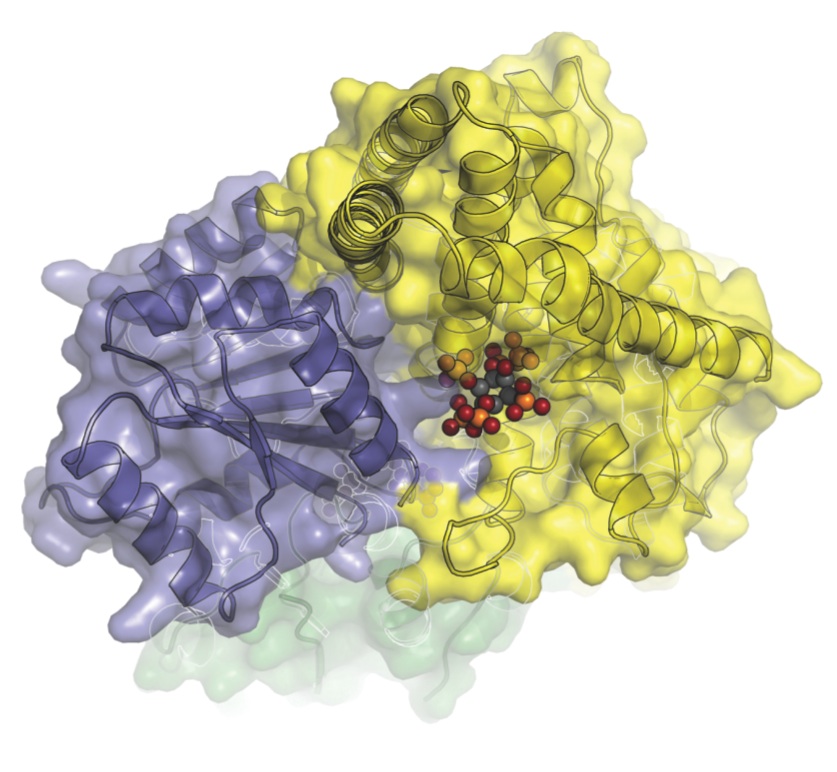 |
| The closest look yet at the molecular machinery that helps transport messenger RNA from a cell’s nucleus. In this image, Dbp5 (blue-grey) and Gle1 (yellow) are glued together by IP6 (colored spheres). (Image courtesy of Karsten Weis’ and James Berger’s labs) |
Abstract:
A tiny motor tasked with one of nature's biggest jobs is now better understood. The molecular machinery that helps export messenger RNA from a cell's nucleus has been structurally mapped at the Advanced Light Source, a synchrotron located at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
RNA-Exporting Machine Deciphered at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source
Berkeley, CA | Posted on March 28th, 2011Messenger RNA conveys genetic information from the nucleus to the cell's cytoplasm, where it guides the synthesis of proteins — the workhorses of biology. A key protein complex that helps to ferry messenger RNA from the nucleus has been poorly understood until now, however.
"Our research describes how this protein complex works at the molecular level," says Ben Montpetit, a postdoctoral researcher in Karsten Weis' lab at the University of California, Berkeley. Their research, a collaboration with biochemists Nathan Thomsen and James Berger, also of the University of California, Berkeley, is described in a paper published March 27 in an advance online edition of the journal Nature. Berger is also a faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab's Physical Biosciences Division.
The scientists studied a protein called Dbp5 that resides at the nuclear pore complex of fungi, plant, and animal cells. In these organisms, it reshapes messenger RNA as part of a chain of events required to send it from the nucleus.
But that's just the tip of the iceberg. Dbp5 is among a class of enzymes called DEAD-box ATPase that perform vital RNA-remodeling functions throughout nature, from humans and oak trees to fungi and single-celled bacteria. Understanding how it works in the cells of one species will illuminate how it works in distantly related species.
"DEAD-box proteins are conserved throughout life, so learning how it works in this case sheds light on its function everywhere in nature," says Montpetit.
The scientists conducted their research at beamline 8.3.1 of the Advanced Light Source, a national user facility that generates intense x-rays to probe the fundamental properties of substances. They used the synchrotron to resolve the structure of Dbp5 from yeast cells at key steps of the enzyme's job, such as when it's activated by another protein called Gle1 and when it binds with RNA. The structures were obtained at resolutions of between one and four angstroms (one angstrom is the diameter of a hydrogen atom).
The result is a time-lapse series of the protein's choreographed bid to remodel messenger RNA, with its twists and turns revealed at the highest resolution yet.
Among the team's most intriguing discoveries is the role of a molecule that is known to be involved in messenger RNA transport, but whose function was a mystery. They found that the molecule, called inositol hexakisphosphate, or IP6, tethers Gle1 to Dbp5. This stabilizes the two proteins long enough for Gle1 to kickstart Dbp5 into action.
"IP6 acts like a molecular glue," says Montpetit. "This is one of the first examples of an endogenous small molecule functioning to bring larger protein molecules together. With this knowledge, scientists can now consider how IP6 may be used to regulate mRNA export under various conditions, such as in response to stress."
Their research could also advance scientists' understanding of a rare but devastating family of diseases called lethal congenital contracture syndrome. The mutation that causes this disease is mapped to the genes that produce both Gle1 and IP6. Now, with Gle1's role in messenger RNA transport further elucidated, the door opens for the development of therapies that target its function.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health's National Institute of General Medical Sciences and the G. Harold and Leila Y. Mathers Foundation.
####
About Berkeley Lab
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) national laboratory managed by the University of California for the DOE Office of Science. Berkeley Lab provides solutions to the world’s most urgent scientific challenges including sustainable energy, climate change, human health, and a better understanding of matter and force in the universe. It is a world leader in improving our lives through team science, advanced computing, and innovative technology. Visit our website.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dan Krotz
510-486-4019
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








