Home > Press > Nanotube-Based Filter Cleans Drinking Water - Water Treatment: New filtration system removes bacteria and viruses
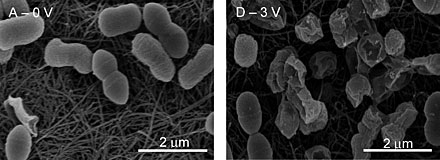 |
| Environ. Sci. Technol. MICROBE ZAPPER When the carbon nanotube-based filter catches bacteria (left), it can also kill them through electrolysis (right). |
Abstract:
For 1 billion people in developing countries, finding clean drinking water is a daily challenge. Now researchers demonstrate a carbon nanotube-based filtration and electrolysis system that can completely remove or inactivate viruses and bacteria from water (Environ. Sci. Technol., DOI: 10.1021/es2000062). Coauthor Chad Vecitis of Harvard University thinks this technology could lead to inexpensive commercial water filters, potentially saving millions every year from diseases and death caused by waterborne pathogens.
Nanotube-Based Filter Cleans Drinking Water - Water Treatment: New filtration system removes bacteria and viruses
Washington, DC | Posted on March 17th, 2011The key filter in the device is a porous film of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compared to other carbon-based filtration techniques, nanotubes have several advantages, Vecitis says, including large surface areas, inherent antimicrobial activity, and resistance to corrosion. By running a small current through the nanotubes and inserting another electrode into the water, the device also can electrolyze water to produce oxygen to kill pathogens.
Vecitis and his colleagues tested their device by pumping suspensions of the bacteria Escherichia coli or of MS2 bacteriophages in a saline solution through the filter assembly. They ran these tests with and without electrolysis.
After one pass through the filter, their device successfully removed all bacteria from the solution, and 99.99% of the viruses. With electrolysis, no viable bacteriophages remained. Since a single virus particle can sicken a person, the researchers consider electrolysis an important step.
Because the electrolysis reaction requires low voltages, portable solar panels could power the device, Vecitis says. To adapt the technology to daily use, he says, the next step would be to create a more-compact device with the capacity to filter 2 to 3 L of water per day, the minimum people need to survive.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © ACS
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








