Home > Press > From Molecule to Object
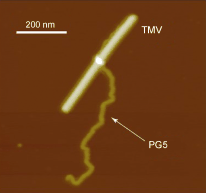 |
| Pushing the limits: A 200×106 Da structurally defined, linear macromolecule (PG5) has a molar mass, cross-section dimension, and cylindrical shape that are comparable to some naturally occurring objects, such as amyloid fibrils or certain plant viruses. The macromolecule is resistant against flattening out on a surface; the picture shows PG5 embracing the tobacco mosaic virus (TMV). |
Abstract:
Largest synthetic structure with molecular precision
From Molecule to Object
Weinheim, Germany | Posted on January 4th, 2011Organic Chemists have always been trying to imitate biology. Although it is possible to make many molecules that imitate biomolecules in terms of structure and function, it remains a challenge to attain the size and form of large biomolecules. An international team led by A. Dieter Schlüter at the ETH Zurich (Switzerland) has now introduced a branched polymer that resembles the tobacco mosaic virus in size and cylindrical form. As the researchers outline in the journal Angewandte Chemie, this is the largest synthetic macromolecule with defined shape and atomic structure reported to date.
Previously, the largest reported synthetic structures with a defined atomic structure were polystyrene polymers with a molecular mass of about 40 million Daltons. However, this value corresponds to a small fraction of the mass of large DNA molecules. Formation of a large synthetic molecule that also has a defined form is much more difficult. For biologists, however, it is routine. Even the simplest organism has a well-defined form, such as the rod-shaped tobacco mosaic virus. For chemists it is a model: a massive molecular ensemble with perfect control over its chemical structure, function, size, and molecular form.
Schlüter and co-workers have now presented a branched polymer that approximates the size and form of the tobacco mosaic virus. Their complex synthesis, which requires 170,000 bond-forming reactions in a single molecule, led to a structurally defined, linear macromolecule with a diameter of about 10 nm and a molecular weight of 200 million Daltons. It thus has a molar mass, cross section, and cylindrical form comparable to the tobacco mosaic virus.
The new macromolecule is a dendronized polymer: it consists of a linear backbone with highly and regularly branched side chains. "This is the biggest synthetic macromolecule with a defined chemical structure and defined form to date," according to Schlüter. "Our experiment is a first step toward the synthesis of molecular objects." A structure is considered to be an object if it keeps its form regardless of its environment, when its interior can be distinguished from the outer environment, and when there is a clear boundary between the two. There are many synthetic nano-objects, however these are not single molecules, but are aggregates of several or many individual molecules.
Author: A. Dieter Schlüter, ETH Zürich (Switzerland), www.polychem.mat.ethz.ch/people/head/dieters
Title: The Largest Synthetic Structure with Molecular Precision: Towards a Molecular Object
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Permalink: dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201005164
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Angewandte Chemie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








