Home > Press > Humble protein, nanoparticles tag-team to kill cancer cells
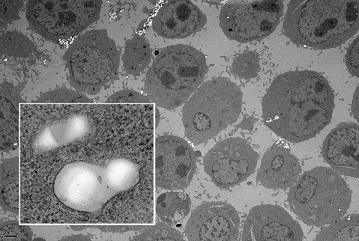 |
| Images of Ramos cells targeted with nanoparticles. Particles carrying human transferrin (white dots, above image and close-up insert) were able to zero in on, attach to and enter cells (grey spheres). |
Abstract:
A normally benign protein found in the human body appears to be able - when paired with nanoparticles - to zero in on and kill certain cancer cells, without having to also load those particles with chemotherapy drugs.
Humble protein, nanoparticles tag-team to kill cancer cells
Chapel Hill, NC | Posted on August 3rd, 2010The finding could lead to a new strategy for targeted cancer therapies, according to the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill scientists who made the discovery.
However, they also cautioned that the result raises concerns about unanticipated "off-target" effects when designing nano-delivery agents.
Transferrin, the fourth most abundant protein in human blood, has been used as a tumor-targeting agent for delivering cancer drugs for almost two decades. The protein's receptor is over-expressed on the surface of many rapidly growing cancers cells, so treatments combined with transferrin ligands are able to seek out and bind to them. Nanoparticles infused with transferrin have long been regarded as safe and nontoxic.
Now, UNC researchers have shown that, surprisingly, attaching transferrin to a nanoparticle surface can effectively and selectively target and kill B-cell lymphoma cells, found in an aggressive form of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It had been thought that nanoparticles would also need to carry toxic chemotherapy agents to have such an effect.
The discovery was made by a team of researchers led by Joseph DeSimone, Ph.D., Chancellor's Eminent Professor of Chemistry in UNC's College of Arts and Sciences and William R. Kenan Jr. Distinguished Professor of Chemical Engineering at North Carolina State University, along with Jin Wang, Ph.D., and Shaomin Tian, Ph.D., in DeSimone's lab. Their findings appear in this week's online issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The scientists say the result is an interesting development in the field of nanomedicine, which researchers hope will eventually provide widely accepted alternatives - or replacements - to chemo and radiation treatment. Those therapies, while considered the most effective methods currently available for tackling cancer, also often damage healthy tissues and organs as a side effect.
Using PRINT (Particle Replication in Non-wetting Templates) technology — a technique invented in DeSimone's lab that allows scientists to produce nanoparticles with well-defined size and shape — the UNC researchers produced biocompatible nanoparticles bonded with human transferrin, and demonstrated that the particles can safely and accurately recognize a broad spectrum of cancers. As well as B-cell lymphoma cells, the particles also effectively targeted non-small cell lung, ovarian, liver and prostate cancer cells.
Generally, the nanoparticles were non-toxic to such cells and should therefore be able to be loaded with standard chemotherapy agents and used to hone in on those cancers.
However, for Ramos cells, an aggressive form of B-cell lymphoma, the transferrin-bonded PRINT nanoparticles not only recognized them but also induced cell death. Meanwhile, free transferrin - which was incubated with Ramos cells but not bound to any nanoparticles - did not kill any Ramos cells, even at high concentrations.
Researchers are carrying out further studies to determine how and why the transferrin-carrying nanoparticles proved toxic to the Ramos cells but not the other tumor types.
"Although this is potentially exciting for the development of entirely new strategies for treating certain types of lymphomas with potentially lower side effects, this study also raises concerns for unanticipated off-target effects when one is designing targeted chemotherapy agents for other types of cancers," said DeSimone. DeSimone is also a member of UNC's Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center and the co-principal investigator for the Carolina Center for Cancer Nanotechnology Excellence. He was also recently appointed as an adjunct member at New York's Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center.
Other UNC coauthors were Robby A. Petros, Ph.D., and Mary E. Napier, Ph.D., from the chemistry department and the Carolina Center for Cancer Nanotechnology Excellence.
The study, "The Complex Role of Multivalency in Nanoparticles Targeting the Transferrin Receptor for Cancer Therapies," was funded by the National Science Foundation; the National Institutes for Health; the Carolina Center for Cancer Nanotechnology Excellence; the William R. Kenan Professorship; Liquidia Technologies; and the North Carolina University Cancer Research Fund, established by the N.C General Assembly to help prevent and treat cancer across the state.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
News Services contact:
Patric Lane
(919) 962-8596
Copyright © University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








