Home > Press > Light, sound, action: The plasmonic promise of graphene
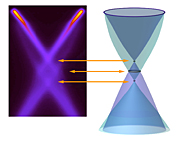 |
| The new graphene band picture indicates how strongly plasmons couple to the charge carriers in graphene. |
Abstract:
Scientists working at the Advanced Light Source (ALS) at DOE's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have discovered striking new details about the electronic structure of graphene, crystalline sheets of carbon just one atom thick. An international team led by Aaron Bostwick and Eli Rotenberg of the ALS found that composite particles called plasmarons play a vital role in determining graphene's properties.
Light, sound, action: The plasmonic promise of graphene
Livermore, CA | Posted on July 7th, 2010"The interesting properties of graphene are all collective phenomena," says Rotenberg, an ALS senior staff scientist responsible for the scientific program at ALS beamline 7, where the work was performed. "Graphene's true electronic structure can't be understood without understanding the many complex interactions of electrons with other particles."
The electric charge carriers in graphene are negative electrons and positive holes, which in turn are affected by plasmons—density oscillations that move like sound waves through the "liquid" of all the electrons in the material. A plasmaron is a composite particle, a charge carrier coupled with a plasmon.
"Although plasmarons were proposed theoretically in the late 1960s, and indirect evidence of them has been found, our work is the first observation of their distinct energy bands in graphene, or indeed in any material," Rotenberg says.
The most striking feature of the recent research is a new band picture for graphene, revealing that the energy bands of graphene cross at three places, not one. The bare-electron picture of graphene shows two conical bands that meet at a single point. But another pair of conical bands, the plasmaron bands, meets at a second, lower Dirac crossing. Between these crossings lies a ring where the hole and plasmaron bands cross.
Understanding the relationships among these three kinds of particles—charge carriers, plasmons, and plasmarons—may hasten the day when graphene can be used for "plasmonics" to build ultrafast computers—perhaps even room-temperature quantum computers—plus a wide range of other tools and applications.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dan Krotz
510.486.4019
Copyright © Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








