Home > Press > Stretching single molecules allows precision studies of interacting electrons
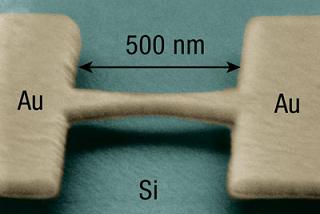 |
| A scanning electron micrograph of a gold bridge suspended 40 nanometers above a silicon substrate. In the experiment, the bridge is severed in the middle, a single molecule is suspended across the gap, and the substrate is bent to stretch the molecule while simultaneously measuring the electron current through the molecule. Credit: Joshua Parks |
Abstract:
Scientists everywhere are trying to study the electrical properties of single molecules. With controlled stretching of such molecules, Cornell researchers have demonstrated that single-molecule devices can serve as powerful new tools for fundamental science experiments. Their work has resulted in detailed tests of long-existing theories on how electrons interact at the nanoscale.
By Anne Ju
Stretching single molecules allows precision studies of interacting electrons
Ithaca, NY | Posted on June 11th, 2010The work, led by professor of physics Dan Ralph, is published in the June 10 online edition of the journal Science. First author is Joshua Parks, a former graduate student in Ralph's lab.
The scientists studied particular cobalt-based molecules with so-called intrinsic spin -- a quantized amount of angular momentum. Theories first postulated in the 1980s predicted that molecular spin would alter the interaction between electrons in the molecule and conduction electrons surrounding it, and that this interaction would determine how easily electrons flow through the molecule. Before now, these theories had not been tested in detail because of the difficulties involved in making devices with controlled spins.
Understanding single-molecule electronics requires expertise in both chemistry and physics, and Cornell's team has specialists in both.
"People know about high-spin molecules, but no one has been able to bring together the chemistry and physics to make controlled contact with these high-spin molecules," Ralph said.
The researchers made their observations by stretching individual spin-containing molecules between two electrodes and analyzing their electrical properties. They watched electrons flow through the cobalt complex, cooled to extremely low temperatures, while slowly pulling on the ends to stretch it. At a particular point, it became more difficult to pass current through the molecule. The researchers had subtly changed the magnetic properties of the molecule by making it less symmetric.
After releasing the tension, the molecule returned to its original shape and began passing current more easily -- thus showing the molecule had not been harmed. Measurements as a function of temperature, magnetic field and the extent of stretching gave the team new insights into exactly what is the influence of molecular spin on the electron interactions and electron flow.
The effects of high spin on the electrical properties of nanoscale devices were entirely theoretical issues before the Cornell work, Ralph said. By making devices containing individual high-spin molecules and using stretching to control the spin, the Cornell team proved that such devices can serve as a powerful laboratory for addressing these fundamental scientific questions.
The study was funded primarily by the National Science Foundation through the Cornell Center for Materials Research, a Materials Research Science and Engineering Center.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact:
Blaine Friedlander
(607) 254-8093
Cornell Chronicle:
Anne Ju
(607) 255-9735
Related Information:
Dan Ralph group people.ccmr.cornell.edu/~ralph/
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








