Home > Press > Boston College scientists create nanoscale coax solar cell
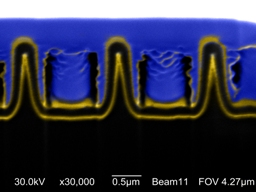 |
| Boston College researchers report their ‘nanocoax’ technology can support a highly efficient thin film solar cell. This image shows a cross section of an array of nanocoax structures, which prove to be thick enough to aborb a sufficient amount of light, yet thin enough to extract current with increased efficiency, the researchers report in the journal Physica Status Solidi. |
Abstract:
Physicists at Boston College have created a nanoscale solar architecture based on the coaxial cable that offers greater efficiency than any previously designed nanotech thin film solar cell, according to their report in the current online edition of the journal Physica Status Solidi.
Boston College scientists create nanoscale coax solar cell
Chestnut Hill, MA | Posted on June 8th, 2010A nano-scale solar cell inspired by the coaxial cable offers greater efficiency than any previously designed nanotech thin film solar cell by resolving the "thick & thin" challenge inherent to capturing light and extracting current for solar power, Boston College researchers report in the current online edition of the journal Physica Status Solidi.
The quest for high power conversion efficiency in most thin film solar cells has been hampered by competing optical and electronic constraints. A cell must be thick enough to collect a sufficient amount of light, yet it needs to be thin enough to extract current.
Physicists at Boston College found a way to resolve the "thick & thin" challenge through a nanoscale solar architecture based on the coaxial cable, a radio technology concept that dates back to the first trans-Atlantic communications lines laid in the mid 1800s.
"Many groups around the world are working on nanowire-type solar cells, most using crystalline semiconductors," said co-author Michael Naughton, a professor of physics at Boston College. "This nanocoax cell architecture, on the other hand, does not require crystalline materials, and therefore offers promise for lower-cost solar power with ultrathin absorbers. With continued optimization, efficiencies beyond anything achieved in conventional planar architectures may be possible, while using smaller quantities of less costly material."
Optically, the so-called nanocoax stands thick enough to capture light, yet its architecture makes it thin enough to allow a more efficient extraction of current, the researchers report in PSS's Rapid Research Letters. This makes the nanocoax, invented at Boston College in 2005 and patented last year, a new platform for low cost, high efficiency solar power.
Constructed with amorphous silicon, the nanocoax cells yielded power conversion efficiency in excess of 8 percent, which is higher than any nanostructured thin film solar cell to date, the team reported.
The ultra-thin nature of the cells reduces the Staebler-Wronski light-induced degradation effect, a major problem with conventional solar cells of this type, according to the team, which included Boston College Professors of Physics Krzysztof Kempa and Zhifeng Ren, as well as BC students and collaborators from Solasta Inc., of Newton, Mass., and École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Institute of Microengineering in Switzerland. The research was funded in part by a Technology Incubator grant from the Department of Energy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ed Hayward, Associate Director, Office of News & Public Affairs, at
Copyright © Boston College
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








