Home > Press > A new study shows that silver nanoparticles mitigate the cell damage caused by ethanol
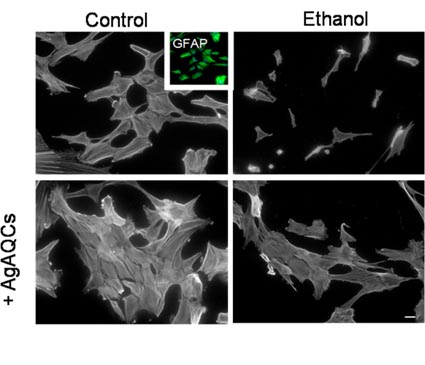 |
| The top left image shows the actin cytoskeleton of the control astrocytes; on the right, cells exposed to ethanol, showing alterations to both the cell morphology and the actin cytoskeleton. The bottom images show the effects of applying silver nanoparticles; on the right, the ethanol causes no alteration of the actin cytoskeleton |
Abstract:
The cover story of the most recent edition of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) describes how nanoparticles formed by very small numbers of silver atoms can protect against the cell damage caused by ethanol. The study was led by researchers from the University of Barcelona and conducted in conjunction with the Magnetism and Nanotechnology laboratory of the University of Santiago de Compostela.
A new study shows that silver nanoparticles mitigate the cell damage caused by ethanol
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on May 26th, 2010"The results of the study show that these clusters of small numbers of silver atoms catalyze ethanol oxidation at similar concentrations to those found in the blood of alcoholics and at values of membrane potential and pH that are compatible with those exhibited by mammalian cells", explains Gustavo Egea, a professor with the Department of Cell Biology, Immunology and Neurosciences of the Faculty of Medicine at the UB and an affiliated researcher for the Institute of Nanosciences and Nanotechnology (IN2UB) and the August Pi i Sunyer Miomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS).
Researchers applied the silver nanoparticles to astrocytes exposed to ethanol. These types of cells accompany neurons and are widely used as models for studying the physiopathological mechanisms of alcohol in foetal alcohol syndrome, a disease that develops in some unborn babies when the mother consumes excessive levels of alcohol and which leads to a range of severe neurological disorders.
Alcohol has particularly harmful effects on nerve cells, and in the specific case of astrocytes it induces programmed cell-death and an alteration of the actin cytoskeleton. Following application of the silver nanoparticles to ethanol-exposed cells, the actin cytoskeleton shows marked improvements and cell-death does not occur. "So, the harmful effect of ethanol on astrocytes is mitigated by the silver nanoparticles, which act as a cytoprotective agent", explains Javier Selva, a lecturer with the Department of Cell Biology, Immunology and Neuroscience and first author of the paper.
The study combines analysis of the electrocatalytic properties of silver nanoparticles with examination of their potential biological applications. "This is a promising field in electrochemistry applied to cell biology, which harnesses the different properties of nanoparticles formed by very small numbers of atoms, referred to generically as atomic clusters", explains Gustavo Egea.
The authors have also found that the nanoparticles prevent alterations induced by other primary alcohols such as methanol and butanol, although not those induced by other toxins such as hydrogen peroxide.
Further information:
Silver sub-nanoclusters electrocatalyze ethanol oxidation and provide protection against ethanol toxicity in cultured mammalian cells. Javier Selva, Susana E. Martínez, David Buceta, María Rodríguez-Vázquez, M. Carmen Blanco, M. Arturo López-Quintela and Gustavo Egea. Journal of the American Chemical Society. DOI: 10.1021/ja907988s - pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja907988s
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © University of Barcelona
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








