Home > Press > Artificial diamonds may make fuel cells more affordable
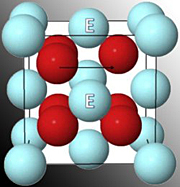 |
| Oxygen (red spheres) migrates from one vacancy to another inside the scandia-doped cubic zirconia. The cations the oxygen must brush past are marked by the letter E. |
Abstract:
Using specialized cubic zirconia or artificial diamonds, scientists from Nanjing Normal University in China and DOE's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory created a membrane that could drop the temperature inside solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs).
Artificial diamonds may make fuel cells more affordable
Richland, WA | Posted on May 11th, 2010Lowering the temperature means these cells could be built from less expensive materials.
Currently, the temperature inside SOFCs is about 1000 degrees Celsius. With this much heat, the cells must be constructed using very durable, very expensive ceramics. Lower temperatures mean the cells could be built from inexpensive stainless steel. The trick to dropping the temperature, and thus the cost, is the membrane at the heart of the cell. The team's new scandia-doped cubic zirconia can work at temperatures as low as 650°C.
This work was done at DOE's EMSL, a national scientific user facility.
####
About Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory
EMSL is funded by DOE's Office of Biological Research, which supports world-class research in the biological, chemical, and environmental sciences to provide innovative solutions to the nation's environmental challenges as well as those related to energy production. EMSL's distinctive focus on integrating computational and experimental capabilities as well as collaborating among disciplines yields a strong, synergistic scientific environment. Bringing together experts and state-of-the-art instruments critical to their research under one roof, EMSL has helped thousands of researchers use a multidisciplinary, collaborative approach to solve some of the most important national challenges in energy, environmental sciences, and human health. These challenges cover a wide range of research, including synthesis, characterization, theory and modeling, dynamical properties, and environmental testing.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kristin Manke
509.372.6011
Copyright © Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








