Home > Press > Brain-like computing on an organic molecular layer
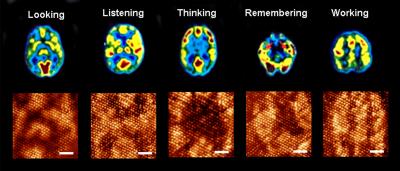 |
| Magnetic resonance images of human brain during different functions appear on top. Similar evolving patterns have been generated on the molecular monolayer one after another (bottom). A snapshot of the evolving pattern for a particular brain function is captured using Scanning Tunneling Microscope at 0.68 V tip bias (scale bar is 6 nm). The input pattern to mimic particular brain function is distinct, and the dynamics of pattern evolution is also typical for a particular brain operation. Credit: Anirban Bandyopadhyay |
Abstract:
Toward intelligent and creative computers
Brain-like computing on an organic molecular layer
Houghton, MI | Posted on April 27th, 2010Information processing circuits in digital computers are static. In our brains, information processing circuits—neurons—evolve continuously to solve complex problems. Now, an international research team from Japan and Michigan Technological University has created a similar process of circuit evolution in an organic molecular layer that can solve complex problems. This is the first time a brain-like "evolutionary circuit" has been realized.
This computer is massively parallel: The world's fastest supercomputers can only process bits one at a time in each of their channels. Their circuit allows instantaneous changes of ~300 bits.
Their processor can produce solutions to problems for which algorithms on computers are unknown, like predictions of natural calamities and outbreaks of disease. To prove this unique feature, they have mimicked two natural phenomena in the molecular layer: heat diffusion and the evolution of cancer cells.
The monolayer has intelligence; it can solve many problems on the same grid.
Their molecular processor heals itself if there is a defect. This remarkable self-healing property comes from the self-organizing ability of the molecular monolayer. No existing man-made computer has this property, but our brain does: if a neuron dies, another neuron takes over its function.
The work is described in the Nature Physics paper "Massively parallel computing on an organic molecular layer." It is coauthored by Ranjit Pati, of the Michigan Technological University Department of Physics. Lead author is Anirban Bandyopadhyay, National Institute for Materials Science, National Institute of Information and Communication Technology, Japan.
####
About Michigan Technological University
Michigan Technological University (mtu.edu) is a leading public research university developing new technologies and preparing students to create the future for a prosperous and sustainable world. Michigan Tech offers more than 130 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in engineering; forest resources; computing; technology; business; economics; natural, physical and environmental sciences; arts; humanities; and social sciences.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Marcia Goodrich
906-487-2343
Copyright © Eurekalert
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








