Home > Press > Spider Silk Reveals a Paradox of Super-strength
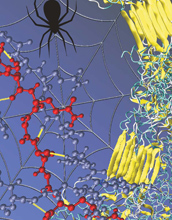 |
| Rendering of the nanoscale structure of silks with beta-sheet nanocrystals shown in yellowish color (right), including a detailed view of the semi-amophous domains between the beta-sheet nanocrystals (left). Credit: Figure courtesy M.J. Buehler (MIT) |
Abstract:
Research finds weakest chemical bonds produce materials stronger than steel
Spider Silk Reveals a Paradox of Super-strength
Arlington, VA | Posted on March 18th, 2010Since its development in China thousands of years ago, silk from silkworms, spiders and other insects has been used for high-end, luxury fabrics as well as for parachutes and medical sutures. Now, National Science Foundation-supported researchers are untangling some of its most closely guarded secrets, and explaining why silk is so super strong.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Center for Materials Science and Engineering say the key to silk's pound-for-pound toughness, which exceeds that of steel, is its beta-sheet crystals, the nano-sized cross-linking domains that hold the material together.
Markus Buehler, the Esther and Harold E. Edgerton Associate Professor in MIT's department of civil and environmental engineering, and his team recently used computer models to simulate exactly how the components of beta sheet crystals move and interact with each other. They found that an unusual arrangement of hydrogen bonds--the "glue" that stabilizes the beta-sheet crystals--play an important role in defining the strength of silk.
They found that hydrogen bonds, which are among the weakest types of chemical bonds, gain strength when confined to spaces on the order of a few nanometers in size. Once in close proximity, the hydrogen bonds work together and become extremely strong. Moreover, if a hydrogen bond breaks, there are still many hydrogen bonds left that can contribute to the material's overall strength, due to their ability to "self-heal" the beta-sheet crystals.
The researchers conclude that silk's strength and ductility--its ability to bend or stretch without breaking--results from this peculiar arrangement of atomic bonds. They say controlling the size of the area in which hydrogen or other chemical bonds act can lead to significantly enhanced properties for future materials, even when the initial chemical bonds are very weak.
The journal Nature Materials reported the findings online March 14.
####
About National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and engineering. In fiscal year (FY) 2010, its budget is about $6.9 billion. NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives over 45,000 competitive requests for funding, and makes over 11,500 new funding awards. NSF also awards over $400 million in professional and service contracts yearly.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contacts
Bobbie Mixon
NSF
(703) 292-8485
Program Contacts
Jorn Larsen-Basse
NSF
(703) 292-7088
Principal Investigators
Markus Buehler
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
(617) 452-2750
Copyright © National Science Foundation
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








