Home > Press > 'Smart' nanoparticles identify, target and kill cancer cells
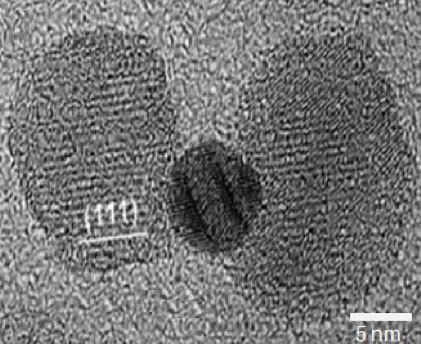 |
| A transmission electron microscope image of a gold hybrid nanoparticle that could be used to treat cancer. The gold in the middle is surrounded by two pieces of iron oxide. Photo by Dickson Kirui. |
Abstract:
Another weapon in the arsenal against cancer has been invented at Cornell: nanoparticles that identify, target and kill specific cancer cells while leaving healthy cells alone.
By Anne Ju
'Smart' nanoparticles identify, target and kill cancer cells
Ithaca, NY | Posted on March 10th, 2010Led by Carl Batt, the Liberty Hyde Bailey Professor of Food Science, the researchers synthesized nanoparticles -- shaped something like a dumbbell -- made of gold sandwiched between two pieces of iron oxide. They then attached antibodies, which target a molecule found only in colorectal cancer cells, to the particles. Once bound, the nanoparticles are engulfed by the cancer cells.
To kill the cells, the researchers use a near-infrared laser, which is a wavelength that doesn't harm normal tissue at the levels used, but the radiation is absorbed by the gold in the nanoparticles. This causes the cancer cells to heat up and die.
The research is reported in the Feb. 15 online edition of the journal Nanotechnology.
"This is a so-called 'smart' therapy," Batt said. "To be a smart therapy, it should be targeted, and it should have some ability to be activated only when it's there and then kills just the cancer cells."
The goal, said lead author and biomedical engineering graduate student Dickson Kirui, is to improve the technology and make it suitable for testing in a human clinical trial. The researchers are now working on a similar experiment targeting prostate cancer cells.
"If, down the line, you could clinically just target the cancer cells, you could then spare the health surrounding cells from being harmed -- that is the critical thing," Kirui said.
Gold has potential as a material key to fighting cancer in future smart therapies. It is biocompatible, inert and relatively easy to tweak chemically. By changing the size and shape of the gold particle, Kirui and colleagues can tune them to respond to different wavelengths of energy.
Once taken up by the researchers' gold particles, the cancer cells are destroyed by heat -- just a few degrees above normal body temperature -- while the surrounding tissue is left unharmed. Such a low-power laser does not have any effect on surrounding cells because that particular wavelength does not heat up cells if they are not loaded up with nanoparticles, the researchers explained.
Using iron oxide -- which is basically rust -- as the other parts of the particles might one day allow scientists to also track the progress of cancer treatments using magnetic resonance imaging, Kirui said, by taking advantage of the particles' magnetic properties.
The work is funded by the Sloan Foundation and the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, which has been a partner with Cornell since 1999 to bring laboratory work to clinical testing.
####
About Cornell University
Once called "the first American university" by educational historian Frederick Rudolph, Cornell University represents a distinctive mix of eminent scholarship and democratic ideals. Adding practical subjects to the classics and admitting qualified students regardless of nationality, race, social circumstance, gender, or religion was quite a departure when Cornell was founded in 1865.
Today's Cornell reflects this heritage of egalitarian excellence. It is home to the nation's first colleges devoted to hotel administration, industrial and labor relations, and veterinary medicine. Both a private university and the land-grant institution of New York State, Cornell University is the most educationally diverse member of the Ivy League.
On the Ithaca campus alone nearly 20,000 students representing every state and 120 countries choose from among 4,000 courses in 11 undergraduate, graduate, and professional schools. Many undergraduates participate in a wide range of interdisciplinary programs, play meaningful roles in original research, and study in Cornell programs in Washington, New York City, and the world over.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact:
Blaine Friedlander
(607) 254-8093
Cornell Chronicle:
Anne Ju
(607) 255-9735
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








