Home > Press > Predicting the Fate of Stem Cells
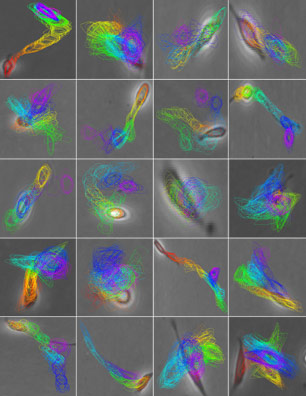 |
| Advanced computer vision technology detects subtle cell movements that are impossible to discern with the human eye. |
Abstract:
New method decodes cell movements, accurately predicts how cells will divide
Predicting the Fate of Stem Cells
Troy, NY | Posted on March 1st, 2010Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have discovered a new method for predicting — with up to 99 percent accuracy — the fate of stem cells.
Using advanced computer vision technology to detect subtle cell movements that are impossible to discern with the human eye, Professor Badri Roysam and his former student Andrew Cohen ‘89 can successfully forecast how a stem cell will split and what key characteristics the daughter cells will exhibit.
By allowing the isolation of cells with specific capabilities, this discovery could one day lead to effective methods for growing stem cells on a large scale for therapeutic use.
"If you have many cells in a culture, they all look the same. But our new method senses all sorts of tiny differences in the shapes and movements of the cells, and uses these cues to predict what kind of cells it will divide into," said Roysam, professor of electrical, computer, and systems engineering at Rensselaer. "We believe this method will be beneficial for one day taking cells from a patient, and then growing large amounts of the kind of cells that patient is in need of. This could enable many new and exciting types of medical treatments using stem cells."
Results of the study, titled "Computational prediction of neural progenitor cell fates," were published recently in the journal Nature Methods.
In order to achieve successful stem cell-based therapies, researchers require access to large amounts of specific cells. This has proven difficult, as there are currently no methods for controlling or manipulating the division of bulk quantities of cells. When stem cells or progenitor cells divide via mitosis, the resulting daughter cells can be self-renewing or terminal. A self-renewing cell will go on to split into two daughter cells, while a terminally differentiated cell is fated to be a specific, specialized cell type. Researchers want the ability to influence this division in order to produce large volumes of the correct type of cells.
Roysam and Cohen tracked the development of rat retinal progenitor cells cultured in their collaborator's laboratory at McGill University. The computer system they developed took images of the cells every five minutes, and employed algorithmic information theoretic prediction (AITP) to observe the behavior of the cells, analyze the behavior, and discern whether each individual cell is fated to split into self-replicating or terminal daughter cells. This process occurs in real time, so researchers know the fate of cells before they actually divide.
The researchers predicted with 99 percent accuracy if the rat retinal progenitor cells would split into self-renewing or specialized cells, and predicted with 87 percent accuracy certain characteristics of the specialized cells.
"Our results suggest that stem cells display subtle dynamic patterns that can be sensed computationally to predict the outcome of their next division using AITP," Roysam said. "In theory, AITP can be used to analyze nearly any type of cell, and could lead to advances in many different fields."
Roysam said prototyping and development of the system leveraged the processing power of Rensselaer's supercomputer, the Computational Center for Nanotechnology Innovations (CCNI).
Co-authors of the paper are Michel Cayouette and Francisco Gomes of the Cellular Neurobiology Research Unit at the Institut de Recherces Cliniques de Monteal; and Roysam's former student Cohen, now an assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
This project was supported in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation Center for Subsurface Sensing and Imaging Systems, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Foundation Fighting Blindness-Canada.
For more information, visit Roysam's Web site at: www.ecse.rpi.edu/~roysam.
####
About Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute is the nation’s oldest technological university. The university offers degrees from five schools: Engineering; Science; Architecture; Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences; and the Lally School of Management & Technology; as well as an interdisciplinary degree in Information Technology.
Institute programs serve undergraduates, graduate students, and working professionals around the world. The Institute’s long-standing reputation drew students from 39 states in addition to Washington, D.C., Puerto Rico, and 13 foreign countries in the fall of 2009.
Rensselaer offers more than 145 programs at the bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral levels. Students are encouraged to work in interdisciplinary programs that allow them to combine scholarly work from several departments or schools. The university provides rigorous, engaging, interactive learning environments and campus-wide opportunities for leadership, collaboration, and creativity.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Mullaney
Phone: (518) 276-6161
Copyright © Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








