Home > Press > Made in IBM Labs: IBM Scientists Demonstrate World's Fastest Graphene Transistor
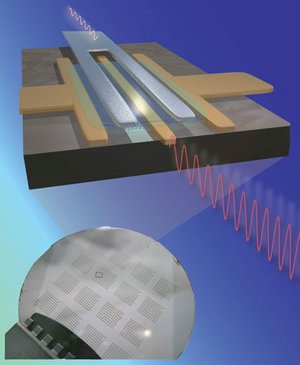 |
| IBM Graphene RF Transistor |
Abstract:
Holds Promise for Improving Performance of Transistors
Made in IBM Labs: IBM Scientists Demonstrate World's Fastest Graphene Transistor
Yorktown Heights, NY | Posted on February 5th, 2010In a just-published paper in the magazine Science, IBM (NYSE: IBM) researchers demonstrated a radio-frequency graphene transistor with the highest cut-off frequency achieved so far for any graphene device - 100 billion cycles/second (100 GigaHertz).
This accomplishment is a key milestone for the Carbon Electronics for RF Applications (CERA) program funded by DARPA, in an effort to develop next-generation communication devices.
The high frequency record was achieved using wafer-scale, epitaxially grown graphene using processing technology compatible to that used in advanced silicon device fabrication.
"A key advantage of graphene lies in the very high speeds in which electrons propagate, which is essential for achieving high-speed, high-performance next generation transistors," said Dr. T.C. Chen, vice president, Science and Technology, IBM Research. "The breakthrough we are announcing demonstrates clearly that graphene can be utilized to produce high performance devices and integrated circuits."
Graphene is a single atom-thick layer of carbon atoms bonded in a hexagonal honeycomb-like arrangement. This two-dimensional form of carbon has unique electrical, optical, mechanical and thermal properties and its technological applications are being explored intensely.
Uniform and high-quality graphene wafers were synthesized by thermal decomposition of a silicon carbide (SiC) substrate. The graphene transistor itself utilized a metal top-gate architecture and a novel gate insulator stack involving a polymer and a high dielectric constant oxide. The gate length was modest, 240 nanometers, leaving plenty of space for further optimization of its performance by scaling down the gate length.
It is noteworthy that the frequency performance of the graphene device already exceeds the cut-off frequency of state-of-the-art silicon transistors of the same gate length (~ 40 GigaHertz). Similar performance was obtained from devices based on graphene obtained from natural graphite, proving that high performance can be obtained from graphene of different origins. Previously, the team had demonstrated graphene transistors with a cut-off frequency of 26 GigaHertz using graphene flakes extracted from natural graphite.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Loughran
IBM Media Relations
914-945-1613
Copyright © IBM
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








