Home > Press > Stopping Bacterial Infections Without Antibiotics
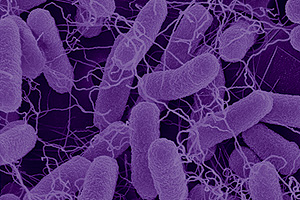 |
| A scanning electron microscopy image of the bacterium Escherichia coli. Many bacteria, including E. coli, "talk" to each other by secreting and perceiving small molecules, a process called quorum sensing. Flagella and appendages that extend out of the cell walls can be produced in response to this signaling. Nearest neighbors control group behavior. Disrupting this intercellular communication could prove to be a new way to fight infection or disease. Courtesy The Bentley Group. |
Abstract:
Clark School's Nanofactories Could Be Next Big Step in Antimicrobial Treatment
Stopping Bacterial Infections Without Antibiotics
College Park, MD | Posted on January 27th, 2010New research at the A. James Clark School of Engineering could prevent bacterial infections using tiny biochemical machines—nanofactories—that can confuse bacteria and stop them from spreading, without the use of antibiotics.
A paper about the research is featured in the current issue of Nature Nanotechnology. "Engineered biological nanofactories trigger quorum sensing response in targeted bacteria," was authored by Clark School alumnus Rohan Fernandes (Ph.D. '08, bioengineering), graduate student Varnika Roy (molecular and cell biology), graduate student Hsuan-Chen Wu (bioengineering), and their advisor, William Bentley (professor and chair, Fischell Department of Bioengineering).
The group's work is an update on their original nanofactories, first developed in 2007. Those nanofactories made use of tiny magnetic bits to guide them to the infection site.
"This is a completely new, all-biological version," he says. "The new nanofactories are self-guided and targeted. We've demonstrated for the first time that they're capable of finding a specific kind of bacterium and inducing it to communicate, a much finer level of automation and control."
The new nanofactories can tell the difference between bad (pathogenic) and good bacteria. For instance, our digestive tracts contain a certain level of good bacteria to help us digest food. The new nanofactories could target just the bad bacteria, without disrupting the levels of good bacteria in the digestive tract (a common side effect of many antibiotics). Nanofactories target the bacteria directly rather than traveling throughout the body, another advantage over traditional antibiotics.
Bacterial cells talk to each other in a form of cell-to-cell communication known as quorum sensing. When the cells sense that they have reached a certain quantity, an infection could be triggered. The biological nanofactories developed at the Clark School can interrupt this communication, disrupting the actions of the cells and shutting down an infection.
Alternatively, the nanofactories could trick the bacteria into sensing a quorum too early. Doing so would trigger the bacteria to try to form an infection before there are enough bacterial cells to do harm. This would prompt a natural immune system response capable of stopping them without the use of drugs.
Because nanofactories are designed to affect communication instead of trying to kill the bacteria, they could help treat illness in cases where a strain of bacteria has become resistant to antibiotics.
"The work by Dr. Bentley is extremely exciting as he is using the ability of engineering to 'build' using nature based components," says Philip Leduc, associate professor in the Departments of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering and the Lane Center for Computational Biology and Biological Sciences at Carnegie Mellon University. "Understanding the science of cells is wonderful, but then using these components and constructing systems that leverage biological advantages is a huge step forward. His work in this paper uses his synthetic biology approach to build new nanofactories toward new areas of antimicrobials as well as opening new findings in quorum sensing."
The nanofactories' ability to alter cell-to-cell communication isn't limited to fighting infections.
"Quorum sensing and signaling molecules are actually used to accomplish a lot of things," Bentley explains. "Sometimes disease develops because communication is not taking place—a good example is digestive disorders that involve an imbalance of bacteria in the digestive tract. In that case, nanofactories could be used to start or increase communication instead of disrupting it."
For More Information:
Read the article at Nature Nanotechnology
www.nature.com/nnano/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nnano.2009.457.html
Visit Professor Bentley's web site
www.bioe.umd.edu/~bentley/
See a research overview at the Biochip Collaborative web site
biochip.umd.edu/bentley/index.html
####
About A. James Clark School of Engineering
The Clark School of Engineering, situated on the rolling, 1,500-acre University of Maryland campus in College Park, Md., is one of the premier engineering schools in the U.S.
The Clark School's graduate programs are collectively the fastest rising in the nation. In U.S. News & World Report's annual rating of graduate programs, the school is 17th among public and private programs nationally, 9th among public programs nationally and first among public programs in the mid-Atlantic region. The School offers 13 graduate programs and 12 undergraduate programs, including degree and certification programs tailored for working professionals.
The school is home to one of the most vibrant research programs in the country. With major emphasis in key areas such as communications and networking, nanotechnology, bioengineering, reliability engineering, project management, intelligent transportation systems and space robotics, as well as electronic packaging and smart small systems and materials, the Clark School is leading the way toward the next generations of engineering advances.
Visit the Clark School homepage at www.eng.umd.edu.
For more information, please click here
Copyright © PrNewswire
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








