Home > Press > Nanoparticles cross blood-brain barrier to enable 'brain tumor painting'
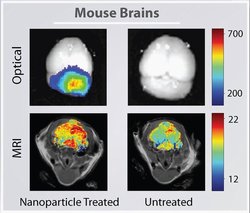 |
| A mouse brain tumor imaged using nanoparticles (left column) or conventional techniques (right column) combined with optical imaging and MRI. The nanoparticles give a clearer picture of the tumor, which is located at the back of the brian in the cerebellum. Image courtesy University of Washington. |
Abstract:
Brain cancer is among the deadliest of cancers. It's also one of the hardest to treat. Imaging results are often imprecise because brain cancers are extremely invasive. Surgeons must saw through the skull and safely remove as much of the tumor as they can. Then doctors use radiation or chemotherapy to destroy cancerous cells in the surrounding tissue.
Nanoparticles cross blood-brain barrier to enable 'brain tumor painting'
Seattle, WA | Posted on August 4th, 2009Researchers at the University of Washington have been able to illuminate brain tumors by injecting fluorescent nanoparticles into the bloodstream that safely cross the blood-brain barrier -- an almost impenetrable barrier that protects the brain from infection. The nanoparticles remained in mouse tumors for up to five days and did not show any evidence of damaging the blood-brain barrier, according to results published this week in the journal Cancer Research.
Results showed the nanoparticles improved the contrast in both MRI and optical imaging, which is used during surgery.
"Brain cancers are very invasive, different from the other cancers. They will invade the surrounding tissue and there is no clear boundary between the tumor tissue and the normal brain tissue," said lead author Miqin Zhang, a UW professor of materials science and engineering.
Being unable to distinguish a boundary complicates the surgery. Severe cognitive problems are a common side effect.
"If we can inject these nanoparticles with infrared dye, they will increase the contrast between the tumor tissue and the normal tissue," Zhang said. "So during the surgery, the surgeons can see the boundary more precisely.
"We call it 'brain tumor illumination or brain tumor painting,'" she said. "The tumor will light up."
Nano-imaging could also help with early cancer detection, Zhang said. Current imaging techniques have a maximum resolution of 1 millimeter (1/25 of an inch). Nanoparticles could improve the resolution by a factor of 10 or more, allowing detection of smaller tumors and earlier treatment.
Until now, no nanoparticle used for imaging has been able to cross the blood-brain barrier and specifically bind to brain-tumor cells. With current techniques doctors inject dyes into the body and use drugs to temporarily open the blood-brain barrier, risking infection of the brain.
The UW team surmounted this challenge by building a nanoparticle that remains small in wet conditions. The particle was about 33 nanometers in diameter when wet, about a third the size of similar particles used in other parts of the body.
Crossing the blood-brain barrier depends on the size of the particle, its lipid, or fat, content, and the electric charge on the particle. Zhang and colleagues built a particle that can pass through the barrier and reach tumors. To specifically target tumor cells they used chlorotoxin, a small peptide isolated from scorpion venom that many groups, including Zhang's, are exploring for its tumor-targeting abilities. On the nanoparticle's surface Zhang placed a small fluorescent molecule for optical imaging, and binding sites that could be used for attaching other molecules.
Future research will evaluate this nanoparticle's potential for treating tumors, Zhang said. She and colleagues already showed that chlorotoxin combined with nanoparticles dramatically slows tumors' spread. They will see whether that ability could extend to brain cancer, the most common solid tumor to affect children.
Merely improving imaging, however, would improve patient outcomes.
"Precise imaging of brain tumors is phenomenally important. We know that patient survival for brain tumors is directly related to the amount of tumor that you can resect," said co-author Richard Ellenbogen, professor and chair of neurological surgery at the UW School of Medicine. "This is the next generation of cancer imaging," he said. "The last generation was CT, this generation was MRI, and this is the next generation of advances."
Other co-authors are Omid Veiseh, Conroy Sun, Chen Fang, Narayan Bhattarai, Jonathan Gunn of the UW's department of materials science and engineering; Forrest Kievit and Kim Du of UW bioengineering; Donghoon Lee of UW radiology; Barbara Pullar of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center; and Jim Olson of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and Seattle Children's Hospital.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Jordyn Dukelow Memorial Fund and the Seattle Children's Hospital Brain Tumor Research Endowment.
####
About University of Washington
Founded in 1861, the University of Washington is one of the oldest state-supported institutions of higher education on the West Coast and is one of the preeminent research universities in the world. Read more about the UW's history >
The UW educates a diverse student body to become responsible global citizens and future leaders through a challenging learning environment informed by cutting-edge scholarship.
We discover timely solutions to the world’s most complex problems and enrich people’s lives throughout our community, the state of Washington, the nation and the world.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Miqin Zhang
206-616-9356
Copyright © University of Washington
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








