Home > Press > Purer water made possible by Sandia advance: A single atom makes a big difference
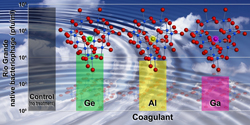 |
| This bar graph shows the efficacy of removing wild-type bacteriophage from Rio Grande water using the all-aluminum coagulant (yellow), the gallium-aluminum coagulant (pink) and a germanium-aluminum coagulant (green). While the gallium-aluminum coagulant is most effective, the germanium-aluminum coagulant is less effective than the all-aluminum coagulant. The gallium makes the active ingredient for binding contaminants more stable and effective, while the germanium, introduced as another variable, was found to make the active ingredient less stable and less effective. |
Abstract:
By substituting a single atom in a molecule widely used to purify water, researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have created a far more effective decontaminant with a shelf life superior to products currently on the market.
Sandia has applied for a patent on the material, which removes bacterial, viral and other organic and inorganic contaminants from river water destined for human consumption, and from wastewater treatment plants prior to returning water to the environment.
Purer water made possible by Sandia advance: A single atom makes a big difference
ALBUQUERQUE, NM | Posted on July 22nd, 2009"Human consumption of ‘challenged' water is increasing worldwide as preferred supplies become more scarce," said Sandia principal investigator May Nyman. "Technological advances like this may help solve problems faced by water treatment facilities in both developed and developing countries."
The study was published in June 2009 in the journal Environmental Science & Technology (a publication of the American Chemical Society) and highlighted in the June 22 edition of Chemical & Engineering News. Sandia is working with a major producer of water treatment chemicals to explore the commercial potential of the compound.
The water-treatment reagent, known as a coagulant, is made by substituting an atom of gallium in the center of an aluminum oxide cluster — itself a commonly used coagulant in water purification, says Nyman.
The substitution isn't performed atom by atom using nanoscopic tweezers but rather uses a simple chemical process of dissolving aluminum salts in water, gallium salts into a sodium hydroxide solution and then slowly adding the sodium hydroxide solution to the aluminum solution while heating.
"The substitution of a single gallium atom in that compound makes a big difference," said Nyman. "It greatly improves the stability and effectiveness of the reagent. We've done side-by-side tests with a variety of commercially available products. For almost every case, ours performs best under a wide range of conditions."
Wide-ranging conditions are inevitable, she said, when dealing with a natural water source such as a river. "You get seasonal and even daily fluctuations in pH, temperature, turbidity and water chemistry. And a river in central New Mexico has very different conditions than say, a river in Ohio."
The Sandia coagulant attracts and binds contaminants so well because it maintains its electrostatic charge more reliably than conventional coagulants made without gallium, itself a harmless addition.
The new material also resists converting to larger, less-reactive aggregates before it is used. This means it maintains a longer shelf life, avoiding the problem faced by related commercially available products that aggregate over time.
"The chemical substitution [of a gallium atom for an aluminum atom] has been studied by Sandia's collaborators at the University of California at Davis, but nobody has ever put this knowledge to use in an application such as removing water contaminants like microorganisms," said Nyman.
The project was conceived and all water treatment studies were performed at Sandia, said Nyman, who worked with Sandia microbiologist Tom Stewart. Transmission electron microscope images of bacteriophages binding to the altered material were achieved at the University of New Mexico. Mass spectroscopy of the alumina clusters in solution was performed at UC Davis.
The work was sponsored by Sandia's Laboratory Directed Research Development office. Ohio."
####
About Sandia National Laboratories
Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin company, for the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration. With main facilities in Albuquerque, N.M., and Livermore, Calif., Sandia has major R&D responsibilities in national security, energy and environmental technologies, and economic competitiveness.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Neal Singer
(505) 845-7078
Copyright © Sandia National Laboratories
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








