Home > Press > Swarming Particles
 |
Abstract:
Silver chloride microparticles act as light-driven micromotors that organize into swarms
Swarming Particles
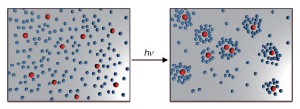
Weinheim, Germany | Posted on April 8th, 2009A swarm of tiny machines, speeding in concert through the bloodstream to repair an organ or deliver a drug to its target area, microrobots working together to construct a nanotechnological component—although it sounds like science fiction, it is a thoroughly realistic future scenario. Amazing progress has already been made in the production of autonomous nano- and micromotors, but the little machines have continued to lack in team spirit. To complete challenging tasks, the individual machines must communicate and cooperate with each other. Researchers led by Ayusman Sen at Pennsylvania State University (USA) have now introduced silver chloride microparticles that can "swarm" together, almost like living single-celled organisms. As reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie, irradiation with UV light causes the particles to give off "signal substances" that "attract" other particles.
Living cells and organisms are able to exchange information with each other to accomplish tasks as a team. Single-celled slime molds, for example, living in unfavorable conditions thus release a special substance. Neighboring slime molds follow the gradient of this signal substance and aggregate in the form of a multi-celled fruiting body. The silver chloride particles used by Sen's team, which are about 1µm in size, behave in a similar fashion when irradiated with UV light. Silver chloride decomposes under UV light, releasing ions that act as both a propulsion mechanism and signal substance.
This phenomenon is based on diffusiophoresis, the movement of particles along an electrolyte gradient. The silver chloride particles "swim" toward a higher ion concentration. Because of irregularities in the surfaces of the particles and non-uniform irradiation, the degradation of the particles is asymmetric. Different quantities of ions are released in different places on the surface, which results in a local ion gradient around the particles. The particle thus produces its own ion gradient, which propels it at speeds up to 100 µm/s (self-diffusiophoresis). Neighboring sliver chloride particles follow the ion gradient of the solution and "swim" to regions of higher particle density. After several minutes, this results in small, stable "swarms" of particles. Photochemically inactive silicon dioxide particles also react to the ion signal, aggregating around the silver chloride particles.
This system can be used as a nonbiological model for communication between cells. Most importantly though, it represents a new design principle for "intelligent" synthetic nano- or micromachines that can work together as a team.
Author: Ayusman Sen, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park (USA), research.chem.psu.edu/axsgroup/dr_sen.html
Title: Schooling Behavior of Light-Powered Autonomous Micromotors in Water
Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2009, 48, No. 18, 3308-3312, doi: 10.1002/anie.200804704
####
About Angewandte Chemie
Introduced in 1997, Wiley InterScience® (www.interscience.wiley.com) is a leading international resource for scientific, technical, medical and scholarly content.
In June 2008, Wiley InterScience incorporated the online content formerly hosted on Blackwell Synergy to provide access to over 3 million articles across 1400 journals. This massive archive, combined with some 7000 OnlineBooks and major reference works—plus industry leading databases such as The Cochrane Library, and the acclaimed Current Protocols laboratory manuals—make Wiley InterScience one of the world's premiere resources for advanced research.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Editorial office:
or
Amy Molnar (US):
or
Jennifer Beal (UK):
or
Alina Boey (Asia):
Copyright © Wiley InterScience
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








