Home > Press > Carbon nanotube avalanche process nearly doubles current
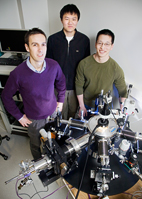 |
| Photo by L. Brian Stauffer Electrical and computer engineering professor Eric Pop, from left, worked with undergraduate Yang Zhao and graduate student Albert Liao, both in ECE, to demonstrate a remarkable increase in the current-carrying capacity of carbon nanotubes. |
Abstract:
By pushing carbon nanotubes close to their breaking point, researchers at the University of Illinois have demonstrated a remarkable increase in the current-carrying capacity of the nanotubes, well beyond what was previously thought possible.
Carbon nanotube avalanche process nearly doubles current
Champaign, IL | Posted on February 9th, 2009The researchers drove semiconducting carbon nanotubes into an avalanche process that carries more electrons down more paths, similar to the way a multilane highway carries more traffic than a one-lane road.
"Single-wall carbon nanotubes are already known to carry current densities up to 100 times higher than the best metals like copper," said Eric Pop, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the U. of I. "We now show that semiconducting nanotubes can carry nearly twice as much current as previously thought."
As reported in the journal Physical Review Letters, the researchers found that at high electric fields (10 volts per micron), energetic electrons and holes can create additional electron-hole pairs, leading to an avalanche effect where the free carriers multiply and the current rapidly increases until the nanotube breaks down.
The sharp increase in current, Pop said, is due to the onset of avalanche impact ionization, a phenomenon observed in certain semiconductor diodes and transistors at high electric fields, but not previously seen in nanotubes.
While the maximum current carrying capacity for metallic nanotubes has been measured at about 25 microamps, the maximum current carrying capacity for semiconducting nanotubes is less established. Previous theoretical predictions suggested a similar limit for single-band conduction in semiconducting nanotubes.
To study current behavior, Pop, graduate student Albert Liao and undergraduate student Yang Zhao first grew single-wall carbon nanotubes by chemical vapor deposition from a patterned iron catalyst. Palladium contacts were used for measurement purposes. The researchers then pushed the nanotubes close to their breaking point in an oxygen-free environment.
"We found that the current first plateaus near 25 microamps, and then sharply increases at higher electric fields," said Pop, who also is affiliated with the Beckman Institute and the Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory at the U. of I. "We performed repeated measurements, obtaining currents of up to 40 microamps, nearly twice those of previous reports."
By inducing very high electric fields in the nanotubes, the researchers drove some of the charge carriers into nearby subbands, as part of the avalanche process. Instead of being in just one "lane," the electrons and holes could occupy several available lanes, resulting in much greater current.
The avalanche process (which cannot be observed in metallic carbon nanotubes because an energy gap is required for electron-hole multiplication) offers additional functionality to semiconducting nanotubes, Pop said. "Our results suggest that avalanche-driven devices with highly nonlinear turn-on characteristics can be fashioned from semiconducting single wall nanotubes."
Funding was provided by the National Science Foundation and the National Institute of Standards and Technology through the Nanoelectronics Research Initiative.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James E. Kloeppel
Physical Sciences Editor
217-244-1073
Eric Pop
217-244-2070
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








