Home > Press > Researcher invents lethal 'lint brush' to capture and kill cancer cells in the bloodstream
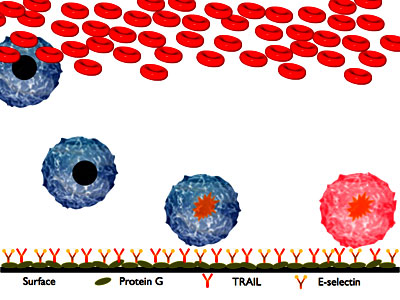 |
| A schematic of the two-receptor cancer neutralization concept. Cancer cells present in blood stick and roll on the selectins on the surface of the device. While rolling they bind to TRAIL and accumulate the self-destruct signal. Once they detach from the surface and leave the device, they will die 1-2 days later. |
Abstract:
In a new tactic in the fight against cancer, Cornell researcher Michael King has developed what he calls a lethal "lint brush" for the blood -- a tiny, implantable device that captures and kills cancer cells in the bloodstream before they spread through the body.
Researcher invents lethal 'lint brush' to capture and kill cancer cells in the bloodstream
ITHACA, NY | Posted on December 16th, 2008The strategy, which takes advantage of the body's natural mechanism for fighting infection, could lead to new treatments for a variety of cancers, said King, who is an associate professor of biomedical engineering.
In research conducted at the University of Rochester and to be published in an upcoming issue of the journal Biotechnology and Bioengineering, King showed that two naturally occurring proteins can work together to attract and kill as many as 30 percent of tumor cells in the bloodstream -- without harming healthy cells.
King's approach uses a tiny tubelike device coated with the proteins that could hypothetically be implanted in a peripheral blood vessel to filter out and destroy free-flowing cancer cells in the bloodstream.
To capture the tumor cells in the blood, King used selectin molecules -- proteins that move to the surface of blood vessels in response to infection or injury. Selectin molecules normally recruit white blood cells (leukocytes) which "roll" along their surfaces and create an inflammatory response -- but they also attract cancer cells, which can mimic the adhesion and rolling process.
Once the cancer cells adhered to the selectin on the microtube's surface, King exposed them to a protein called TRAIL (for Tumor Necrosis Factor Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand), which binds to two so-called "death receptors" on the cancer cells' surface, setting in motion a process that causes the cell to self-destruct.
The TRAIL then releases the cells back into the bloodstream to die; and the device is left free to work on new cells.
"It's a little more sophisticated than just filtering the blood, because we're not just accumulating cancer cells on the surface," King said.
King's research showed that the device can capture and kill about 30 percent of cancer cells flowing past it a single time, with the potential to kill more in the closed-loop system of the body. Used in combination with traditional cancer therapies, King said, the device could remove a significant proportion of metastatic cells, "and give the body a fighting chance to remove the rest of them."
The team also showed that a system in which the cancer cells "roll" over the target molecules - presenting their entire surface to the molecules - is four times more effective than a static setup in which the cells and proteins make contact at a single point.
King's group tested the device on prostate and colon cancer cells, but noted that it could also be customized with additional peptides or other proteins to target other types of cancer cells. "And if you could reduce or prevent metastasis, pretty much any cancer would be treatable," he said.
But translating the research into a clinical application will take time, he added, and is still likely years away.
"The actual physical device, when it gets eventually tested in humans, will probably look a lot like an arteriovenous shunt [a small tube, or shunt, that diverts blood flow] with our protein coating," he said.
"This has never been tried before. It's a whole new way of approaching cancer treatment," he added. "There's a lot of work yet to be done, of course, before this actually helps people -- but this is how it starts."
Other authors on the paper include Kuldeep Rana, a Cornell Ph.D. student, and Jane Liesveld, M.D., a clinician at the University of Rochester. The research was funded by New York state and the National Cancer Institute.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lauren Gold
(607) 255-9736
Media Contact:
Blaine Friedlander
(607) 254-8093
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








