Home > Press > FSU physicists take part in discovery of new subatomic particle
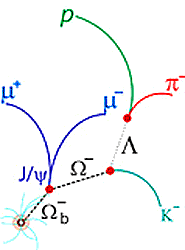 |
| Omega sub-b particle |
Abstract:
It's not every day that scientists discover a new particle of matter. Florida State University physicists were part of just such a historic event recently while collaborating with researchers from 18 countries at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab).
The Batavia, Ill., laboratory on Sept. 3 announced the discovery of a new subatomic particle, dubbed Omega-sub-b. Scientists involved in Fermilab's giant DZero Experiment said the newly found particle is an exotic relative of the proton and has about six times the proton's mass.
FSU physicists take part in discovery of new subatomic particle
Tallahassee, FL | Posted on September 18th, 2008"Measuring the properties of the Omega-sub-b brings scientists a step closer to understanding the force that binds quarks together to form matter," said Horst Wahl, an FSU physics professor who takes part in the ongoing DZero Experiment.
"This is a very beautiful and significant result in high-energy physics," said Mark Riley, chairman of FSU's physics department. "Another piece of nature's particle physics puzzle has been found. Many congratulations to the FSU High Energy Physics group and their DZero collaborators!"
The DZero Experiment is a worldwide collaboration of scientists conducting research on the fundamental nature of matter. About 600 physicists from 90 institutions located all over the world are taking part in the experiment, headquartered at Fermilab's Tevatron Collider, until the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the world's premier high-energy accelerator, is fully operational. (The LHC, located at CERN, the European Laboratory for Particle Physics, in Geneva, Switzerland, conducted its first major test on Sept. 10 when it fired a beam of protons around a 17-mile tunnel.)
Quarks -- the constituents of protons, neutrons and more than 200 other subatomic particles -- come in six "flavors": up and down, charm and strange, and bottom and top. The proton, for example, has two up quarks and a down quark. When the DZero team went through about 100 trillion proton-antiproton collisions from the Tevatron Collider, it found 18 events that carried the signature of the "doubly strange" Omega-sub-b, which is composed of two strange quarks and a bottom quark. The mass of the particle was close to what theorists had predicted.
Fermilab says the Omega-sub-b is a relative of the famous Omega-minus, which is made up of three strange quarks and was discovered back in 1964. Finding the strange-strange-bottom combination fills in one more slot in what scientists consider a "periodic table" of quark combinations. It also confirms that one of the scientific world's most successful theories, the Standard Model of particle physics, is on the right track.
"We can't observe quarks directly, only the particles that they form. This discovery is another confirmation of the beauty of the Standard Model," said Susan Blessing, an FSU physics professor who participates in the DZero Experiment. "The Omega-sub-b has been predicted for a long time, and it is good to see it observed experimentally."
Members of FSU's High Energy Physics group who also participate in the DZero Experiment are Professor Harrison Prosper; Associate Professor Todd Adams; Staff Physicist Sharon Hagopian; postdoctoral research associates Andrew Askew, Oleksiy Atramentov and Jadranka Sekaric; and graduate students Daniel Duggan, Edgar Carrera, Trang Hoang and Suharyo Sumowidagdo.
In addition, FSU theorists Jeff Owens, Laura Reina and Bernd Berg are experts in calculations in QCD, the theory of strong interactions that govern the interaction of quarks.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Florida State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








