Home > Press > Nanotech Fuel Cell Research May Clear Hydrogen Hurdles
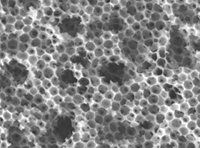 |
| This nano-scale honeycomb structure enables more efficient chemical reactions in a new generation of fuel cells. (click for high-res version)
(Photo: Yannick C. Kimmel, an undergraduate student in the School of Engineering and Applied Science who is working on this research) |
Abstract:
Fuel cells are one of the most touted new energy technologies. They directly convert the chemical energy of fuels into electrical energy, doing so roughly twice as efficiently as a diesel engine.
The biggest stumbling block preventing the widespread adoption of fuel cell technology has been a reliance on hydrogen as the "fuel." Not only is hydrogen both difficult and dangerous to store and distribute, but 96 percent of hydrogen comes from oil and gas. Fuel cells that rely on hydrogen do little to reduce fossil fuel use.
New research from a University of Virginia team, recently funded by a new U.Va. Collaborative Sustainable Energy Seed Grant worth about $30,000, is taking two approaches to removing the need for hydrogen.
Nanotech Fuel Cell Research May Clear Hydrogen Hurdles
Charlottesville, VA | Posted on August 5th, 2008The twin projects will both use similar nano-scale engineering in very different applications, explained team member Steve McIntosh, an assistant professor of chemical engineering. One half of the project will apply new nano-scale structures to try and create a new type of "solar cell" that will gather the energy of sunlight to electrochemically split water into its molecular components of oxygen and hydrogen, which could potentially provide a practically limitless, renewable source of hydrogen.
The other half of the research will use similar nano-scale structures to bypass hydrogen and create a new type of fuel cell that can transform renewable biofuels like biodiesel directly into electricity.
"There's not going to be a silver bullet to solve the problem, so we've got to pursue multiple approaches," McIntosh said.
The nano-scale surface structures being developed are hundreds of times smaller and more precise than existing technology, which offers several expected advantages, McIntosh said. For instance, nano-scale surface structures will make the ion reactions much quicker and more efficient. "It's very important to control the issues down at that scale where everything is happening," McIntosh noted.
More efficient chemical reactions may allow these new fuel cells - known as direct-hydrocarbon solid oxide fuel cells - to operate at much lower temperatures (500 degrees Celsius instead of 800), making them more stable and longer-lasting, McIntosh said.
The goal is a fuel cell that can produce 10,000 hours of electricity to be used in a new type of small power plant, which would provide enough power for a small town or even a city block. A distributed power grid based on such plants would be more efficient than our current power grid.
Even though nano-technology seems to have great potential to improve these types of solar and fuel cells, so far only one paper on this topic has been published, said McIntosh, who last year won a $400,000 National Science Foundation (NSF) Faculty Early Career Development grant for his pioneering work on fuel cells.
His U.Va. collaborators on the current research project are Despina Louca, an associate professor of physics, and Giovanni Zangari, an associate professor of materials science and engineering. Zangari is an expert on the "solar cell" half of the project. Louca will use neutron diffraction equipment at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee to measure how the nanoscale structures work over time.
Any improvements in fuel cell technology are highly sought after and should quickly attract further research dollars from agencies like the U.S. Department of Energy, or the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which has put out a request for a portable power generator that uses fuel cells running directly on diesel fuel, McIntosh said.
In the meantime, he said, this seed grant "gets people motivated and gets them going."
####
About University of Virginia
The University of Virginia is recognized as a leading institution in humanities, social sciences, and arts scholarship. We are now committed to enhancing research in key interdisciplinary areas of science and engineering. In building these complementary strengths, we cultivate a University research culture that supports innovation and ultimately leads to discoveries that will transform society.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
H. Brevy Cannon IV
General Assignments Writer
(434) 243-0368
Copyright © University of Virginia
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








