Home > Press > Nanotube-producing Bacteria Show Manufacturing Promise
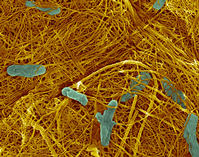 |
| Genus Shewanella. The nanotube filaments produced by biological means could point toward semiconductor manufacturing processes with a smaller energy and environmental footprint. Image credit: Hor-Gil Hur, GIST |
Abstract:
Nanotubes may have high-tech applications, study involving UCR engineers reports
Nanotube-producing Bacteria Show Manufacturing Promise
RIVERSIDE, CA | Posted on December 7th, 2007Two engineers at the University of California, Riverside are part of a binational team that has found semiconducting nanotubes produced by living bacteria - a discovery that could help in the creation of a new generation of nanoelectronic devices.
The research team believes this is the first time nanotubes have been shown to be produced by biological rather than chemical means. It opens the door to the possibility of cheaper and more environmentally friendly manufacture of electronic materials.
Study results appear in today's issue of the early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The team, including Nosang V. Myung, associate professor of chemical and environmental engineering in the Bourns College of Engineering, and his postdoctoral researcher Bongyoung Yoo, found the bacterium Shewanella facilitates the formation of arsenic-sulfide nanotubes that have unique physical and chemical properties not produced by chemical agents.
"We have shown that a jar with a bug in it can create potentially useful nanostructures," Myung said. "Nanotubes are of particular interest in materials science because the useful properties of a substance can be finely tuned according to the diameter and the thickness of the tubes."
The whole realm of electronic devices which power our world, from computers to solar cells, today depend on chemical manufacturing processes which use tremendous energy, and leave behind toxic metals and chemicals. Myung said a growing movement in science and engineering is looking for ways to produce semiconductors in more ecologically friendly ways.
Two members of the research team, Hor-Gil Hur and Ji-Hoon Lee from Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Korea, first discovered something unexpected happening when they attempted to remediate arsenic contamination using the metal-reducing bacterium Shewanella. Myung, who specializes in electro-chemical material synthesis and device fabrication, was able to characterize the resulting nano-material.
The photoactive arsenic-sulfide nanotubes produced by the bacteria behave as metals with electrical and photoconductive properties. The researchers report that these properties may also provide novel functionality for the next generation of semiconductors in nano- and opto-electronic devices.
In a process that is not yet fully understood, the Shewanella bacterium secretes polysacarides that seem to produce the template for the arsenic sulfide nanotubes, Myung explained. The practical significance of this technique would be much greater if a bacterial species were identified that could produce nanotubes of cadmium sulfide or other superior semiconductor materials, he added.
"This is just a first step that points the way to future investigation," he said. "Each species of Shewanella might have individual implications for manufacturing properties."
Myung, Yoo, Hur and Lee were joined in the research by Min-Gyu Kim, Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Pohang, Korea; Jongsun Maeng and Takhee Lee, GIST; Alice C. Dohnalkova and James K. Fredrickson, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, Wash.; and Michael J. Sadowsky, University of Minnesota.
The Center for Nanoscale Innovation for Defense provided funding for Myung's contribution to the study.
####
About University of California, Riverside
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment of about 17,000 is projected to grow to 21,000 students by 2010. The campus is planning a medical school and already has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Graduate Center. With an annual statewide economic impact of nearly $1 billion, UCR is actively shaping the region's future. To learn more, visit http://www.ucr.edu or call (951) UCR-NEWS.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Iqbal Pittalwala
Phone: 951.827.6050
Jim Dexter
dir. of communications
Bourns College of Engin.
Judy Chappell
Bourns College of Engineering
Copyright © University of California, Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Chemical and Environmental Engineering
Chemical and Environmental Engineering
| Related News Press |
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








