Home > Press > Quantum simulation: Particle behavior near the event horizon of block hole
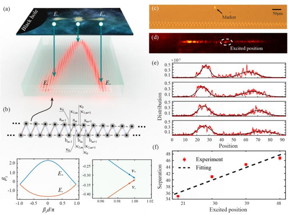 |
| (a) The schematic of mapping the behavior of fermion pair into a photonic lattice. (b) The designed bi-layer waveguide lattice and the corresponding dispersion relation. (c) The cross-section profile of the fabricated lattices. (d) The imagined output probability distribution of single-photon wave packet splitting to two parts and moving in opposite direction. (e) The output probability distributions with different excited positions in the same lattice. (f) The separation distance increases with the excited position linearly. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
The vast universe can always arise people's infinite imagination and yearning. Black hole, as one of the most attractive heavenly bodies in the universe, are waiting to be explored and studied. However, due to the limitations of technology, human is still unable to go into the depths of universe, let alone reach the vicinity of a black hole.
Quantum simulation: Particle behavior near the event horizon of block hole
Beijing, China | Posted on July 16th, 2020Fortunately, based on the equivalence between the metric of curved space-time in general relativity and the electromagnetic parameters in electromagnetic materials, the physical scientist has developed the method of transformation optics to simulate the curved space-time of gravitational field. Now, the scientist is able to study and demonstrate the evolution of particles in curved space-time experimentally. However, up to now, these simulations are limited either in classical regime or in flat space whereas quantum simulation related with general relativity is rarely involved. In the quantum field related with the gravitational effect, there are many striking phenomena, such as Hawking radiation.
Recently, Yao Wang and Xianmin Jin from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Chong Sheng and Hui Liu from the Nanjing University made an exciting progress in observing particle behavior near the event horizon of block hole.
Based on femtosecond laser direct write technology, the waveguide on-site energy and the coupling between waveguides can be well controlled. Inspired by the concept of transformation optics, the team successfully constructed a one-dimensional artificial black hole using a single-layer non-uniform-coupling photonic waveguide lattice. Comparing to linear time evolution in the flat space, the dynamic behavior of single-photon wave packets near the horizon of a black hole accelerates exponentially, and its exponential index depends on the curvature of the black hole.
The team further designed the two-layer photonic waveguide lattice and experimentally observed the acceleration, generation, and evolution of fermion pairs near the event horizon of the black hole: a single-photon packet with positive energy successfully escaped from the black hole, while a single-photon packet with negative energy was captured. The result, which deviates from the intuition that photons are always trapped by black holes, is found well analogue to Hawking radiation which completely origins from quantum effects associated with gravitational effects. Due to vacuum fluctuations, particle-antiparticle pairs are generated near the event horizon of the black hole. Particles with negative energy fall into the black hole, while particles with negative energy escape. This causes the black hole to lose mass, and it would appear that the black hole has just emitted a particle.
Finally, the team think that higher-dimensional curved space-time can be constructed based on the experimental platform. For example, a two-dimensional waveguide array can be used to simulate three-dimensional space-time, and a two-dimensional waveguide array with photon polarization or frequency can be used to simulate four-dimensional space-time. Furthermore, due to the propagation direction plays the role as the time in our experimental platform, dynamics metric can also be emulated based on this experimental platform, such as FRW metric, a model describing cosmic expansion as time evolution, and gravitational wave, which is the ripple of spacetime.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Xian-Min Jin
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








