Home > Press > Macroscopic quantum interference in an ultra-pure metal
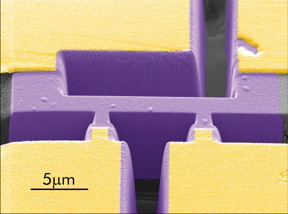 |
| Scanning electron microscope image of a PdCoO2 microstructure to measure c-axis resistivity. CREDIT © MPI CPfS |
Abstract:
That visible light holds the character of a wave can be demonstrated in simple optics experiments, or directly witnessed when rainbows appear in the sky. Although the subtle laws of quantum mechanics, that is, wave mechanics, ultimately govern all the processes of electron transportelectrons in solids, their wave-like nature of the electrons is not often apparent to the casual observer. A classical picture of electrons as solid particles goes surprisingly far in explaining electric currents in metals. As high school students see in experiments with water waves, and we observe and use with light waves in many optical devices, interference is a fundamental property associated with wave-like behavior. Indeed, Davisson and Germer's famous observation of interference in experiments with dilute beams of electrons, nearly a century ago, gave key experimental support to the correctness of the then-new quantum theory.
Macroscopic quantum interference in an ultra-pure metal
Dresden, Germany | Posted on June 26th, 2020In experiments on solids, however, signatures of quantum interference are rare and hard to observe. This is essentially because there are so many electrons, and so many ways in which they can be 'scrambled up', that most interference effects are invisible to experiments that probe distances of more than a few atomic spacings.
One of the themes of research in the Physics of Quantum Materials department is the study of exotic strange layered metals from a structural class with the equally strange name 'delafossites', stemming from the famous French crystallographer Gabriel Delafosse. They are notable because they conduct electricity incredibly well. Indeed, at room temperature one of them, PtCoO2, is the best electrical conductor ever discovered. As part of our research on the delafossites, we were studying how the conduction perpendicular to the layers depends on magnetic field, in crystals that had been sculpted into particular geometries using a focused ion beam (see Fig. 1). To our complete surprise, we observed strong oscillations in this conductivity, of a kind that are a signature of some kindsignaling of interference (see Fig. 2). After a long period of follow-up experiments at this institute and in the new group of our former colleagues Philip Moll and Carsten Putzke, now at EPFL in Lausanne, we collaborated with theorists Takashi Oka and Roderich Moessner in our neighbour institute in Dresden and Ady Stern from the Weizmann Institute in Israel to propose an explanation for what is going on. Remarkably, it requires a form of quantum coherence over macroscopic distances of up to 50000 atomic lattice spacings. It is only observable because of the remarkable purity of the delafossites, whose origin we established in another set of experiments, also published recently. High quality materials continue to hold a wealth of surprises and delights for those who make and study them!
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Carsten Putzke
Copyright © Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








