Home > Press > Tiny particle, big payoff: Innovative virus research may save wheat and other crops
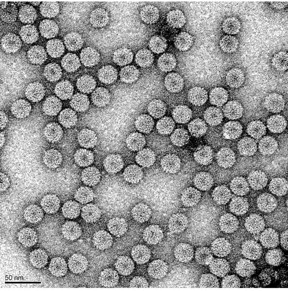 |
| Visually indistinguishable particles of Brome Mosaic Virus. CREDIT Ayala Rao/UCR |
Abstract:
UC Riverside scientists have solved a 20-year-old genetics puzzle that could result in ways to protect wheat, barley, and other crops from a devastating infection.
Tiny particle, big payoff: Innovative virus research may save wheat and other crops
Riverside, CA | Posted on May 15th, 2020Ayala Rao, professor of plant pathology and microbiology, has been studying Brome Mosaic virus for decades. Unlike some viruses, the genetic material of this virus is divided into three particles that until now were impossible to tell apart.
"Without a more definitive picture of the differences between these particles, we couldn't fully understand how they work together to initiate an infection that destroys food crops," Rao said. "Our approach to this problem has brought an important part of this picture into very clear focus."
A paper describing the work Rao's team did to differentiate these particles was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Inside each of the particles is a strand of RNA, the genetic material that controls the production of proteins. The proteins perform different tasks, some of which cause stunted growth, lesions, and ultimately death of infected host plants.
Two decades ago, scientists used the average of all three particles to create a basic description of their structure. In order to differentiate them, Rao first needed to separate them, and get them into their most pure form.
Using a genetic engineering technique, Rao's team disabled the pathogenic aspects of the virus and infused the viral genes with a host plant.
"This bacterium inserts its genome into the plant's cells, similar to the way HIV inserts itself into human cells," Rao said. "We were then able to isolate the viral particles in the plants and determine their structure using electron microscopes and computer-based technology."
Now that one of the particles is fully mapped, it's clear the first two particles are more stable than the third.
"Once we alter the stability, we can manipulate how RNA gets released into the plants," Rao said. "We can make the third particle more stable, so it doesn't release RNA and the infection gets delayed."
This work was made possible by a grant from the University of California Multicampus Research Program and Initiatives. Professors Wiliam Gelbart and Hong Zhou of UCLA, as well as graduate students Antara Chakravarthy of UCR and Christian Beren of UCLA, made significant contributions to this project.
Moving forward, Rao is hoping to bring the other two viral particles into sharper focus with the expertise of scientists at UCLA and UC San Diego.
Brome Mosaic virus primarily affects grasses such as wheat and barley, and occasionally affects soybeans as well. According to Rao, it is nearly identical to Cucumber Mosaic virus, which infects cucumbers as well as tomatoes and other crops that are important to California agriculture.
Not only could this research lead to the protection of multiple kinds of crops, it could advance the understanding of any virus.
"It is much easier to work with plant viruses because they're easier and less expensive to grow and isolate," Rao said. "But what we learn about the principles of replication are applicable to human and animal viruses too."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jules Bernstein
951-827-4580
@UCRiverside
Copyright © University of California - Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








