Home > Press > A filter for cleaner qubits
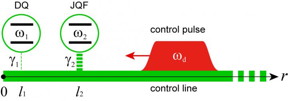 |
| Schematic of a Josephson quantum filter (JQF). The data qubit (DQ) to be protected and the JQF are directly coupled to a semi-infinite waveguide, through which control pulses for the DQ are applied. CREDIT Department of Physic, College of Liberal Arts and Sciences,TMDU |
Abstract:
Researchers at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), RIKEN, and the University of Tokyo propose an improved method for isolating the qubits in a quantum computer from the external environment, which may help usher in the era of practical quantum computing
A filter for cleaner qubits
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on March 6th, 2020A research team at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), RIKEN, and the University of Tokyo have demonstrated how to increase the lifetime of qubits inside quantum computers by using an additional "filter" qubit. This work may help make higher fidelity quantum computers that can be used in financial, cryptographic, and chemistry applications.
Quantum computers are poised to make a large impact in a variety of fields, from internet security to drug development. Instead of being limited to binary 0s and 1s of classical computers, the qubits in quantum computers can take on values that are arbitrary superpositions of the two. This allows quantum computers the potential to solve certain problems, like cracking cryptographic ciphers, much faster than current machines.
However, there is a fundamental tradeoff between the lifetime of the qubit superpositions and the processing speed. This is because the qubits must be carefully shielded from interacting with the environment, or the fragile superposition will snap back to being just a one or zero in a process called decoherence. To delay this loss of quantum fidelity, qubits in quantum computers are coupled only weakly to the control line through which the qubit control pulses are applied. Unfortunately, such a weak coupling limits the speed that computations can be run.
Now, the team at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) theoretically show how coupling a second "filter" qubit to the control line can greatly reduce the noise and spontaneous radiative losses that lead to decoherence. This allows the connections to be strong, which lends itself to faster cycle times.
"In our solution, the filter qubit acts like a nonlinear mirror, which completely reflects radiation from the qubit due to destructive interference but transmits strong control pulses due to absorption saturation" says first author Kazuki Koshino.
This research helps bring about a future in which quantum computers can be found in every business and research lab. Many operational research firms would like to use quantum computers to solve optimization problems that were considered too intensive for conventional computers, while chemists would like to use them to simulate the motion of atoms inside molecules.
"Quantum computers are improved day by day by companies including IBM and Google. As they become faster and more robust, they can be even more widespread," says senior author Yasunobu Nakamura.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kazuki KOSHINO
Copyright © Tokyo Medical and Dental University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








