Home > Press > An 'exceptionally stable' single-atom catalyst: Single platinum atoms stabilized in C12A7 crystals
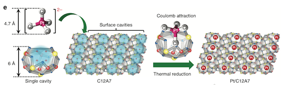 |
| Figure 1. Single platinum atoms stabilized in C12A7 crystals Interaction between negatively charged ions and positively charged surface cavities of C12A7 for effective stabilization of single platinum atoms. |
Abstract:
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have shown that single platinum atoms trapped in C12A7 crystals act as a stable and effective catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitroarenes, an essential process in the production of many kinds of fine chemicals. Their approach could become a versatile route for developing other single-atom catalysts for wide-ranging industrial applications.
An 'exceptionally stable' single-atom catalyst: Single platinum atoms stabilized in C12A7 crystals
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on February 26th, 2020Single-atom catalysts (SACs) are on the way to becoming dream catalysts ― ones that exhibit superb performance based on optimized usage of metal atoms. Many research teams around the world have been working to advance the scalable development of SACs since they were first proposed by Tao Zhang and colleagues in China and the US in 2011.
Now, in a proof-of-concept study that throws the door wide open to developing a new range of SACs, researchers at Tokyo Tech have designed and tested a catalyst composed of single platinum atoms trapped in C12A7, a nanoporous crystal widely used in the production of aluminous cement.
The inner structure of C12A7 crystals is "just the right size" for trapping single metal atoms, the researchers say in their paper published in Nature Communications.
"Our approach is rather like a 'diamond-in-a-ring' strategy, where the surface cavity of C12A7 can be regarded as a ring, and the single platinum atom is fixed on the ring as a diamond," says first author Tian-Nan Ye at Tokyo Tech's Materials Research Center for Element Strategy.
Ye explains that C12A7 has a positively charged framework structure composed of twelve sub-nanometer-sized cages, each with an inner diameter of around 0.4 nanometers ― a suitable size for capturing individual metal atoms. Each cage has a positive charge of +1/3, and the surface cavities have an open 'mouth' that can trap single metal atoms through electronic interaction.
The catalyst has been demonstrated to be highly stable and active toward the selective hydrogenation of nitroarenes, an important process often used in the dye and polymer industries. It has a higher turnover frequency (up to 25772 per hour) than that of platinum-based catalysts unsupported by C12A7. Remarkably, the new catalyst even works at temperatures of up to 600°C.
Based on these promising results, the researchers investigated whether the trapping effect might work using other metals. As they predicted, C12A7 was also capable of capturing single atoms of ruthenium and rhodium, indicating that their strategy would be applicable to various transition metals.
"Our findings open countless doors to developing new kinds of SACs for different catalytic processes," says Ye. Due to its exceptionally high thermal stability, the C12A7 support would be able to withstand harsher conditions involved in other industrially important processes such as ammonia synthesis and CO2 reduction.
Ye points out that the development of SACs cannot be separated from the exploration of new materials. This is a key reason why Professor Hideo Hosono's group at Tokyo Tech is uniquely positioned to be a pioneer in SAC research, he says, building on a series of achievements including the development of novel semiconductors, an iron-based superconductor, and the first room-temperature-stable electride.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Tokyo Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








