Home > Press > Gold nanoclusters: new frontier for developing medication for treatment of Alzheimer's disease
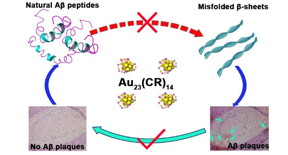 |
| Au23(CR)14 Nanocluster functions in multiple stages of the progression from Aβ monomer to Aβ plaques. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by amyloid-β (Aβ) fibrillation and plaque formation. While more than 50 millions of people are devastated by AD, no treatment is available. Recently, anti-Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy has failed in clinical trials, partially due to the increased cytotoxicity of soluble Aβ oligomers. Therefore, developing a medication for AD treatment becomes an even more grave challenge.
Gold nanoclusters: new frontier for developing medication for treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Beijing, China | Posted on February 14th, 2020In a new research article published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, scientists at the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Materials Synthesis and Processing, Wuhan University of Technology in China explored the possibility of treating with gold nanoclusters.
As illustrated in Figure 1, Au23(CR)14, a novel gold nanocluster modified with Cys-Arg (CR) dipeptide, functions in multiple stages of the progression from Aβ monomer to Aβ plaques: inhibiting the misfolding and fibrillation of amyloid-β (Aβ), fully dissolving the preformed/mature Aβ fibrils and restoring the conformation of Aβ peptides from misfolded β-sheets into unfolded monomer state with abolished cytotoxicity, and more importantly, completely dissolving endogenous Aβ plaques in the brain slices from transgenic AD model mice. Furthermore, Au23(CR)14 has good biocompatibility and infiltration ability across the blood brain barrier (BBB).
This article not only presents a compelling nanotherapeutic candidate for AD treatment, but also opens a new frontier for developing nanomaterial-based medications for AD treatment. Undoubtedly, more researches studying the basic mechanisms by which gold nanoclusters dissolve Aβ plaques will spur the development of new medications for AD treatment.
###
This research received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21975191, 21805218, 51873168, 81803515, 51533007 and 51521001) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2018CFA002 and 2018CFB348).
####
About Science China Press
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country's rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Taolei Sun
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








