Home > Press > A New Old Therapy: A controlled phage therapy can target drug-resistant bacteria while sidestepping potential unintended consequences
 |
Abstract:
The fight against drug-resistant pathogens remains an intense one. While the Centers for Disease Control’s (CDC) 2019 “biggest threats” report reveals an overall decrease in drug-resistant microbe-related deaths as compared to its previous report (2013) the agency also cautions that new forms of drug-resistant pathogens are still emerging.
A New Old Therapy: A controlled phage therapy can target drug-resistant bacteria while sidestepping potential unintended consequences
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on January 13th, 2020Meanwhile, the options for treating infections by these germs are diminishing, confirming doctors’ and scientists’ worries about the end of the age of antibiotics.
“We knew it was going to be a problem early on,” said UC Santa Barbara chemistry and biochemistry professor Irene Chen. “Basically as soon as penicillin was discovered, a few years later it was reported that there was a resistant organism.” Thanks to factors such as horizontal gene transfer and rapid reproduction, organisms such as Gram-negative bacteria are able to evolve faster than we can produce antibiotics to control them.
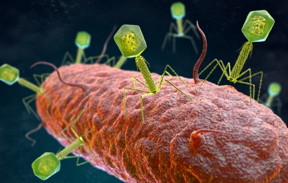
So Chen and her research group are seeking alternatives to antibiotics, in a growing effort to head off the tide of incurable bacterial infections. In their work, the group has turned to bacteriophages, a naturally occurring group of viruses that colonize on bacteria.
“That’s their natural function, really, to grow on and kill bacteria,” said Chen, author of a paper that appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. By taking advantage of the bacteriophages’ ability to home in on specific bacteria without damaging the rest of the microbiome, the researchers were able to use a combination of gold nanorods and near-infrared light to destroy even multidrug-resistant bacteria without antibiotics.
Phage therapy isn’t new, Chen said. In fact, it has been used in the former Soviet Union and Europe for about a century, though they are seen largely as last-resort alternatives to antibiotics. Among the unresolved issues of phage therapy is the incomplete characterization of the phages’ biology — a biology that could allow for unintended consequences due to the phages’ own rapid evolution and reproduction, as well as potential toxins the viruses may carry. Another issue is the all-or-nothing aspect of phage therapy, Chen added.
“It’s difficult to analyze the effect of a phage treatment,” she said. “You might see it completely work or you might see it completely fail, but you don’t have the kind of dose response you want.”
To surmount these challenges, the Chen lab developed a method of controlled phage therapy.
“What we did was to conjugate the phages to gold nanorods,” she explained. These “phanorods” were applied to bacteria on in-vitro cultures of mammalian cells and then exposed to near-infrared light.
“When these nanorods are photo-excited, they translate the energy from light to heat,” Chen said, “and that creates very high local temperatures.”
The heat is enough to kill the bacteria, and it also kills the phages, preventing any unwanted further evolutions. The result is a guided missile of targeted phage therapy that also allows for dosage control. The lab found success in destroying E. coli, P. aeruginosa and V. cholerae — human pathogens that cause acute symptoms if left unchecked. They also were able to successfully destroy X. campestris, a bacteria that causes rot in plants.
In a collaboration with UC Santa Barbara mechanical engineer Beth Pruitt, the lab determined that while the heat successfully destroyed bacteria and phage, more than 80% of the mammalian cell culture underneath the bacteria biofilm survived.
“This issue of whether it damages mammalian tissues is very important,” Chen said. “Work in nanotechnology and nanomedicine treating bacterial infections indicates that when it’s non-targeted, it really does burden the surrounding tissues.”
The lab plans to investigate other possible phages to counter other bacteria, possibly engineering a photothermal method that could treat multiple bacterial infections.
Research on this study was conducted also by UCSB postdoctoral fellow Huan Peng (lead author), Raymond E. Borg and Liam P. Dow.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sonia Fernandez
(805) 893-4765
Shelly Leachman
(805) 893-8726
Copyright © University of California, Santa Barbara
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








