Home > Press > A quantum breakthrough brings a technique from astronomy to the nano-scale: Multi-messenger approach allows scientists to probe electronic and magnetic materials at ultra-small length scales
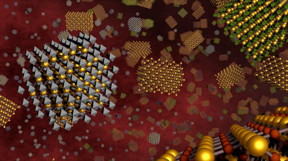 |
| The discovery of multi-messenger nanoprobes allows scientists to simultaneously probe multiple properties of quantum materials at nanometer-scale spatial resolutions. CREDIT Ella Maru Studio |
Abstract:
Researchers at Columbia University and University of California, San Diego, have introduced a novel "multi-messenger" approach to quantum physics that signifies a technological leap in how scientists can explore quantum materials.
A quantum breakthrough brings a technique from astronomy to the nano-scale: Multi-messenger approach allows scientists to probe electronic and magnetic materials at ultra-small length scales
New York, NY | Posted on January 3rd, 2020The findings appear in a recent article published in Nature Materials, led by A. S. McLeod, postdoctoral researcher, Columbia Nano Initiative, with co-authors Dmitri Basov and A. J. Millis at Columbia and R.A. Averitt at UC San Diego.
"We have brought a technique from the inter-galactic scale down to the realm of the ultra-small," said Basov, Higgins Professor of Physics and Director of the Energy Frontier Research Center at Columbia. Equipped with multi-modal nanoscience tools we can now routinely go places no one thought would be possible as recently as five years ago."
The work was inspired by "multi-messenger" astrophysics, which emerged during the last decade as a revolutionary technique for the study of distant phenomena like black hole mergers. Simultaneous measurements from instruments, including infrared, optical, X-ray and gravitational-wave telescopes can, taken together, deliver a physical picture greater than the sum of their individual parts.
The search is on for new materials that can supplement the current reliance on electronic semiconductors. Control over material properties using light can offer improved functionality, speed, flexibility and energy efficiency for next-generation computing platforms.
Experimental papers on quantum materials have typically reported results obtained by using only one type of spectroscopy. The researchers have shown the power of using a combination of measurement techniques to simultaneously examine electrical and optical properties.
The researchers performed their experiment by focusing laser light onto the sharp tip of a needle probe coated with magnetic material. When thin films of metal oxide are subject to a unique strain, ultra-fast light pulses can trigger the material to switch into an unexplored phase of nanometer-scale domains, and the change is reversible.
By scanning the probe over the surface of their thin film sample, the researchers were able to trigger the change locally and simultaneously manipulate and record the electrical, magnetic and optical properties of these light-triggered domains with nanometer-scale precision.
The study reveals how unanticipated properties can emerge in long-studied quantum materials at ultra-small scales when scientists tune them by strain.
"It is relatively common to study these nano-phase materials with scanning probes. But this is the first time an optical nano-probe has been combined with simultaneous magnetic nano-imaging, and all at the very low temperatures where quantum materials show their merits," McLeod said. "Now, investigation of quantum materials by multi-modal nanoscience offers a means to close the loop on programs to engineer them."
###
The study, "Multi-messenger nanoprobes of hidden magnetism in a strained manganite," was developed with support from Programmable Quantum Materials, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the United States Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Science and Basic Energy Sciences.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Carla Cantor
212-854-5276
@columbia
Copyright © Columbia University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








