Home > Press > Nanopores can identify the amino acids in proteins, the first step to sequencing
 |
Abstract:
While DNA sequencing is a useful tool for determining what’s going on in a cell or a person’s body, it only tells part of the story. Protein sequencing could soon give researchers a wider window into a cell’s workings. A new study demonstrates that nanopores can be used to identify all 20 amino acids in proteins, a major step toward protein sequencing.
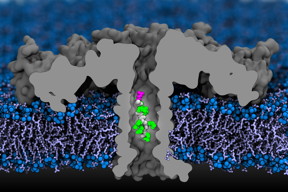
In this computer simulation, a portion of a protein moves through an aerolysin nanopore. The researchers used detailed simulations that mapped each atom, and confirmed their findings experimentally.
Video courtesy of Aleksei Aksimentiev
Nanopores can identify the amino acids in proteins, the first step to sequencing
Champaign, IL | Posted on December 18th, 2019Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Cergy-Pontoise University in France and the University of Freiburg in Germany published the findings in the journal Nature Biotechnology.
“DNA codes for many things that can happen; it tells us what is potentially possible. The actual product that comes out – the proteins that do the work in the cell – you can’t tell from the DNA alone,” said Illinois physics professor Aleksei Aksimentiev, a co-leader of the study. “Many modifications happen along the way during the process of making protein from DNA. The proteins are spliced, chemically modified, folded, and more.”
A DNA molecule is itself a template designed for replication, so making copies for sequencing is relatively easy. For proteins, there is no such natural machinery by which to make copies or to read them. Adding to the difficulty, 20 amino acids make up proteins, as compared with the four bases in DNA, and numerous small modifications can be made to each amino acid during protein production and folding.
“Many amino acids are very similar,” Aksimentiev said. “For example, if you look at leucine and isoleucine, they have the same atoms, the same molecular weight, and the only difference is that one structure is the mirror image of the other.”
Nanopores, small protein channels embedded in a membrane, are a popular tool for DNA sequencing. Previously, scientists thought that the differences in amino acids were too small to register with nanopore technology. The new study shows otherwise.
The researchers used a membrane channel naturally made by bacteria, called aerolysin, as their nanopore. In both computer modeling and experimental work, they chopped up proteins and used a chemical carrier to drive the amino acids into the nanopore. The carrier molecule also kept the amino acids inside the pore long enough for it to register a measurable difference in the electrical signature of each amino acid – even leucine and isoleucine, the mirror-image twins.
“This work builds confidence and reassures the nanopore community that protein sequencing is indeed possible,” said Abdelghani Oukhaled, a professor of biophysics at Cergy-Pontoise whose team carried out much of the experimental work.
The researchers found they could further differentiate modified forms of amino acids by using a more sensitive measurement apparatus or by treating the protein with a chemical to improve differentiation. The measurements are precise enough to potentially identify hundreds of modifications, Aksimentiev said, and even more may be recognized by tweaking the pore.
“This is a proof-of-concept study showing that we can identify the different amino acids,” he said. “The current method for protein characterization is mass spectrometry, but that does not determine the sequence; it compares a sample to what’s already in the database. Its ability to characterize new variations or mutations is limited. With nanopores, we finally could look at those modifications which have not yet been studied.”
The aerolysin nanopore could be integrated into standard nanopore setups, Aksimentiev said, making it accessible to other scientists. The researchers are now exploring approaches to read the amino acids in sequential order as they are cut from the protein. They also are considering other applications for the system.
“One potential application would be to combine this with immunoassays to fish out proteins of interest and then sequence them. Sequencing them will tell us whether they’re modified or not, and that could lead to a clinical diagnostic tool,” Aksimentiev said.
“This work shows that there’s really no limit to how precisely we can characterize biological molecules,” he said. “Very likely, one day we will be able to tell the molecular makeup of the cell – what we are made of, down to the level of individual atoms.”
The National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation supported this work. Computer modeling was done on the Blue Waters supercomputer at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the U. of I.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Aleksei Aksimentiev, call 217-333-6495; email
LIZ AHLBERG TOUCHSTONE | BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES EDITOR | 217-244-1073
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








