Home > Press > In a quantum future, which starship destroys the other? Quantum physicists blur the lines of cause and effect, illustrating how a sequence of events can flip and co-exist at the same time
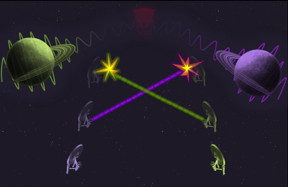 |
| A starship exercise where two ships fire at each other. In a quantum future, an evil being can place planet in superposition near one ship or the other, leading to both starships simultaneously destroying each other. CREDIT Magdalena Zych, Igor Pikovski |
Abstract:
Quantum mechanics boasts all sorts of strange features, one being quantum superposition - the peculiar circumstance in which particles seem to be in two or more places or states at once. Now, an international group of physicists led by Stevens Institute of Technology, University of Vienna and University of Queensland flip that description on its head, showing that particles are not the only objects that can exist in a state of superposition - so can time itself.
In a quantum future, which starship destroys the other? Quantum physicists blur the lines of cause and effect, illustrating how a sequence of events can flip and co-exist at the same time
Hoboken, NJ | Posted on August 23rd, 2019"The sequence of events can become quantum mechanical," said co-author Igor Pikovski, a physicist at the Center for Quantum Science and Engineering at Stevens Institute of Technology. " We looked at quantum temporal order where there is no distinction between one event causing the other or vice versa."
The work, reported in the August 22 issue of Nature Communications, is among the first to reveal the quantum properties of time, whereby the flow of time doesn't observe a straight arrow forward, but one where cause and effect can co-exist both in the forward and backward direction. In the upcoming era of quantum computers, the work holds particular promise: quantum computers that exploit the quantum order of performing operations might beat devices that operate using only fixed sequences.
To show this scenario, Pikovski and colleagues merged two seemingly conflicting theories - quantum mechanics and general relativity - to conduct a Gedanken experiment, a way of using the imagination to investigate the nature of things. The team, consisting of Pikovski, Magdalena Zych, Fabio Costa and Caslav Brukner, started by asking the question, "what would a clock measure if it was influenced by a massive object in a quantum superposition state, i.e. both near and far at the same time?"
According to general relativity, the presence of a massive object slows down the flow of time, such that a clock placed close to a massive object will run slower compared to an identical one that is farther away.
To illustrate what happens, imagine a pair of starships training for a mission. They are asked to fire at each other at a specified time and dodge the fire at another time, whereby each ship knows the exact time when to fire and when to dodge. If either ship fires too early, it will destroy the other, and this establishes an unmistakable time order between the firing events.
However, if a powerful agent could place a sufficiently massive object, say a planet, closer to one ship it would slow down its flow of time. As a result, the ship would dodge the fire too late and would be destroyed.
Quantum mechanics complicates the matter. When placing the planet in a state of superposition near one ship or the other, both can be destroyed or survive at the same time. The sequence of events exists in a state of superposition, such that each starship simultaneously destroys the other.
The authors illustrate for the first time how this quantum scenario can occur and how it can be verified. "Moving planets around is hard," said Pikovski. "But imagining it helped us examine a quantum aspect of time that was previously unknown."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Thania Benios
917-930-5988
Copyright © Stevens Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








