Home > Press > Army project may advance quantum materials, efficient communication networks
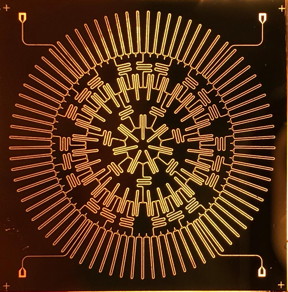 |
| A US Army project at Princeton University results in an electronic array on a microchip that simulates particle interactions in a hyperbolic place, a geometric surface in which space curves away from itself at every point. CREDIT Princeton University |
Abstract:
A U.S. Army project exploring novel applications of superconducting resonators has discovered these systems may be used to simulate quantum materials impossible to otherwise fabricate. Additionally, they may provide insights to open and fundamental questions in quantum mechanics and gravity.
Army project may advance quantum materials, efficient communication networks
Research Triangle Park, NJ | Posted on July 25th, 2019Scientists at Princeton University, led by electrical engineering Professor Andrew Houck, built an electronic array on a microchip that simulates particle interactions in a hyperbolic plane, a geometric surface in which space curves away from itself at every point.
"This research may advance quantum simulation in a way that enables us to not only develop a better understanding of materials relevant to Army goals, but also help us explore questions at the forefront of other fields of Army relevance," said Dr. Sara Gamble, a program manager with the Army Research Office, an element of the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command's Army Research Laboratory. "In addition to the potential materials applications, the fantastic results obtained by the research team can provide insight into communication networks and ultimately enable the DOD to develop more efficient networking capabilities."
The research, published in Nature, used superconducting circuits to create a lattice that functions as a hyperbolic space. When the researchers introduce photons into the lattice, they can answer a wide range of difficult questions by observing the photons' interactions in simulated hyperbolic space.
"The problem is that if you want to study a very complicated quantum mechanical material, then computer modeling is very difficult," said Dr. Alicia Kollár, a postdoctoral research associate at the Princeton Center for Complex Materials. "We're trying to implement a model at the hardware level so that nature does the hard part of the computation for you."
The centimeter-sized chip is etched with a circuit of superconducting resonators that provide paths for microwave photons to move and interact. The resonators on the chip are arranged in a lattice pattern of heptagons, or seven-sided polygons. The structure exists on a flat plane, but simulates the unusual geometry of a hyperbolic plane.
"In normal 3-D space, a hyperbolic surface doesn't exist," said Princeton electrical engineering Prof. Andrew Houck. "This material allows us to start to think about mixing quantum mechanics and curved space in a lab setting."
Trying to force a three-dimensional sphere onto a two-dimensional plane reveals that space on a spherical plane is smaller than on a flat plane. This is why the shapes of countries appear stretched out when drawn on a flat map of the spherical Earth. In contrast, a hyperbolic plane would need to be compressed in order to fit onto a flat plane.
To simulate the effect of compressing hyperbolic space onto a flat surface, the researchers used a special type of resonator called a coplanar waveguide resonator. When microwave photons pass through this resonator, they behave in the same way whether their path is straight or meandering. The meandering structure of the resonators offers flexibility to "squish and scrunch" the sides of the heptagons to create a flat tiling pattern, said Kollár, who is starting a faculty position at the University of Maryland and Joint Quantum Institute.
Looking at the chip's central heptagon is akin to looking through a fisheye camera lens, in which objects at the edge of the field of view appear smaller than in the center -- the heptagons look smaller the farther they are from the center. This arrangement allows microwave photons that move through the resonator circuit to behave like particles in a hyperbolic space.
The chip's ability to simulate curved space could enable new investigations in quantum mechanics, including properties of energy and matter in the warped space-time around black holes. The material could also be useful for understanding complex webs of relationships in mathematical graph theory and communication networks. Kollár noted that this research could eventually aid the design of new materials.
But first, she and her colleagues will need to further develop the photonic material, both by continuing to examine its mathematical basis and by introducing elements that enable photons in the circuit to interact.
"By themselves, microwave photons don't interact with each other -- they pass right through," Kollár said. Most applications of the material would require "doing something to make it so that they can tell there's another photon there."
"The research team is forming connections with researchers in other disciplines because of these results, and the addition of photon interactions into the systems will increase the application space for advancing Army capabilities even further," Gamble said.
####
About U.S. Army Research Laboratory
The CCDC Army Research Laboratory (ARL) is an element of the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command. As the Army's corporate research laboratory, ARL discovers, innovates and transitions science and technology to ensure dominant strategic land power. Through collaboration across the command's core technical competencies, CCDC leads in the discovery, development and delivery of the technology-based capabilities required to make Soldiers more lethal to win our Nation's wars and come home safely. CCDC is a major subordinate command of the U.S. Army Futures Command.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lisa Bistreich-Wolfe
919-549-4372
Copyright © U.S. Army Research Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Quantum communication
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








