Home > Press > Dresden physicists use nanostructures to free photons for highly efficient white OLEDs: Trapped light particles
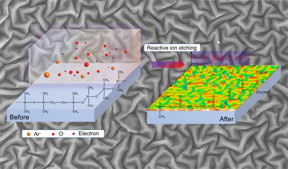 |
| Principle of reactive ion etching for the generation of quasi-periodic nanostructures. CREDIT (c) Sebastian Reineke et al., Nature Communications: CC BY 4.0 |
Abstract:
Since light-emitting diodes only produce monochrome light, manufacturers use various additive colour-mixing processes to produce white light.
Dresden physicists use nanostructures to free photons for highly efficient white OLEDs: Trapped light particles
Dresden, Germany | Posted on July 12th, 2019Since the first development of white OLEDs in the 1990s, numerous efforts have been made to achieve a balanced white spectrum and high luminous efficacy at a practical luminance level. However, the external quantum efficiency (EQE) for white OLEDs without additional outcoupling techniques can only reach 20 to 40 percent today. About 20 percent of the generated light particles (photons) remain trapped in the glass layer of the device. The reason for this is the total internal reflection of the particles at the interface between glass and air.
Further photons are waveguided in the organic layers, while others get ultimately lost at the interface to the top metal electrode.
Numerous approaches have been investigated to extract the trapped photons from OLEDs. An international research team led by Dr. Simone Lenk and Prof. Sebastian Reineke from the TU Dresden has now presented a new method for freeing the light particles in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
The physicists introduce a facile, scalable and especially lithography-free method for the generation of controllable nanostructures with directional randomness and dimensional order, significantly boosting the efficiency of white OLEDs. The nanostructures are produced by reactive ion etching. This has the advantage that the topography of the nanostructures can be specifically controlled by adjusting the process parameters.
In order to understand the results obtained, the scientists have developed an optical model that can be used to explain the increased efficiency of OLEDs. By integrating these nanostructures into white OLEDs, an external quantum efficiency of up to 76.3% can be achieved.
For Dr. Simone Lenk, the new method opens up numerous new avenues: "We had been looking for a way to specifically manipulate nanostructures for a long time already. With reactive ion etching, we have found a cost-effective process that can be used for large surfaces and is also suitable for industrial use. The advantage lies in the fact that the periodicity and height of the nanostructures can be completely adjusted via the process parameters and that thus an optimal outcoupling structure for white OLEDs could be found. These quasi-periodic nanostructures are not only suitable as outcoupling structures for OLEDs, but also have the potential for further applications in optics, biology and mechanics".
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Sebastian Reineke
49-351-463-38686
Copyright © Technische Universitšt Dresden
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








