Home > Press > Electron-behaving nanoparticles rock current understanding of matter: Discovery will lead to new methods for materials design
 |
Abstract:
•When nanoparticles modified with DNA in colloidal crystals reach a critical size, they behave like electrons
•Researchers call this behavior ‘metallicity’ because it’s similar to how electrons migrate in metals
•Researcher: ‘It’s really rare in science to discover a new property, but that’s what happened here’
Electron-behaving nanoparticles rock current understanding of matter: Discovery will lead to new methods for materials design
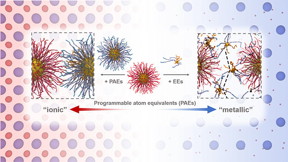
Evanston, IL | Posted on June 20th, 2019It’s not an electron. But it sure does act like one.
Northwestern University researchers have made a strange and startling discovery that nanoparticles engineered with DNA in colloidal crystals — when extremely small — behave just like electrons. Not only has this finding upended the current, accepted notion of matter, it also opens the door for new possibilities in materials design.
“We have never seen anything like this before,” said Northwestern’s Monica Olvera de la Cruz, who made the initial observation through computational work. “In our simulations, the particles look just like orbiting electrons.”
With this discovery, the researchers introduced a new term called “metallicity,” which refers to the mobility of electrons in a metal. In colloidal crystals, tiny nanoparticles roam similarly to electrons and act as a glue that holds the material together.
“This is going to get people to think about matter in a new way,” said Northwestern’s Chad Mirkin, who led the experimental work. “It’s going to lead to all sorts of materials that have potentially spectacular properties that have never been observed before. Properties that could lead to a variety of new technologies in the fields of optics, electronics and even catalysis.”
The paper will publish Friday, June 21 in the journal Science.
Olvera de la Cruz is the Lawyer Taylor Professor of Materials Science and Engineering in Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering. Mirkin is the George B. Rathmann Professor of Chemistry in Northwestern’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences.
Mirkin’s group previously invented the chemistry for engineering colloidal crystals with DNA, which has forged new possibilities for materials design. In these structures, DNA strands act as a sort of smart glue to link together nanoparticles in a lattice pattern.
“Over the past two decades, we have figured out how to make all sorts of crystalline structures where the DNA effectively takes the particles and places them exactly where they are supposed to go in a lattice,” said Mirkin, founding director of the International Institute of Nanotechnology.
In these previous studies, the particles’ diameters are on the tens of nanometers length scale. Particles in these structures are static, fixed in place by DNA. In the current study, however, Mirkin and Olvera de la Cruz shrunk the particles down to 1.4 nanometers in diameter in computational simulations. This is where the magic happened.
“The bigger particles have hundreds of DNA strands linking them together,” said Olvera de la Cruz. “The small ones only have four to eight linkers. When those links break, the particles roll and migrate through the lattice holding together the crystal of bigger particles.”
When Mirkin’s team performed the experiments to image the small particles, they found that Olvera de la Cruz’s team’s computational observations proved true. Because this behavior is reminiscent to how electrons behave in metals, the researchers call it “metallicity.”
“A sea of electrons migrates throughout metals, acting as a glue, holding everything together,” Mirkin explained. “That’s what these nanoparticles become. The tiny particles become the mobile glue that holds everything together.”
Olvera de la Cruz and Mirkin next plan to explore how to exploit these electron-like particles in order to design new materials with useful properties. Although their research used gold nanoparticles, Olvera de la Cruz said “metallicity” applies to other classes of particles in colloidal crystals.
“In science, it’s really rare to discover a new property, but that’s what happened here,” Mirkin said. “It challenges the whole way we think about building matter. It’s a foundational piece of work that will have a lasting impact.”
The research, “Particle analogs of electrons in colloidal crystals,” was supported by the Center for Bio-Inspired Science, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (award number DE-SC0000989); the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (award number FA9550-17-1-0348); the Office of Naval Research (award number 00014-15-1-0043) and the Sherman Fairchild Foundation. Martin Girard, a PhD graduate from Olvera de la Cruz’s laboratory and current postdoctoral scholar at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research in Germany, is the paper’s first author.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Amanda Morris
847-467-6790
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








