Home > Press > New record: 3D-printed optical-electronic integration
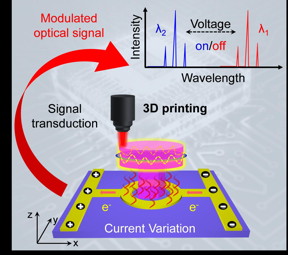 |
| Schematic illustration of an integrated electrically controlled microlaser module for optoelectronic hybrid integration. Briefly, this module is designed to be a thermo-responsive polymer resonator on top of a chip-scale metal heating circuit. The voltage is applied in-plane with the current transport to provide local-area thermal field, which induces the lasing wavelength change of the upper dye-doped microresonators. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Optoelectronic integration offers a promising strategy to simultaneously obtain the merits of electrons and photons when they serve as information carriers, including high-density communication and high-speed information processing, paving the way for the next-generation integrated circuits (ICs). The ever-increasing demand on bandwidth and information density in ICs call for the micro/nano functional devices capable of being fabricated in three-dimensional (3D) ICs, which is desirable for their improved performance in data processing under lower consumption. In such highly integrated circuits, however, selective electrical modulation of specific micro/nanoscale optical devices, including light sources and waveguides, is a key requirement for yielding more functional and more compact integrated elements, but hindered by the normal used nonlinearity found in electro-optic materials.
New record: 3D-printed optical-electronic integration
Beijing, China | Posted on June 18th, 2019
Femtosecond laser direct writing (FsLDW), as one of the 3D printing techniques, enables the direct and addressable construction of 3D-integrated optoelectronic devices utilizing organic compounds with two-photon polymerized features. With doping flexibility, the polymerized microstructures can be readily incorporated with organic dye molecules to produce functional devices, like coherent laser sources. Besides, organic polymers possess excellent responsiveness to external stimuli, including temperature. Their large thermo-optic coefficient enables the realization of the electrical tuning of resonant wavelength with high efficiency when they are fabricated into microcavity structures. The incorporation of thermo-responsive polymeric microlaser with underneath electrical microheater in the 3D fabrication manner can be used as an effective hybrid microlaser module with selective electric modulation towards optical-electronic integration.
Very recently, Professor Yong Sheng Zhao's group in the Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences demonstrated an in situ electrically modulated microlaser module based on 3D-printed dye-doped polymeric microdisks, which is published in Science China Chemistry.
The thermo-optic effect of the polymer matrix enabled the tuning of lasing modes from the microdisk upon heating. The shape designability of FsLDW allows the fabrication of higher-level microstructures to manipulate light signals, including the waveguide coupled microdisks for light remote control and the coupled double-microdisk resonators for laser mode selection. The latter microstructure was further integrated with an underneath electrical microheater.
As a result, the cavity resonant wavelength can be shifted on the basis of resistance heating controlled optical length change through the thermo-optic effect of polymeric matrix material, which enabled an electrical modulation of the output wavelength of the 3D-printed microlaser module.
###
This work was supported financially by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2017YFA0204502), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21533013 and 21790364).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Zhao Yong Sheng
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








