Home > Press > Drilling speed increased by 20% – yet another upgrade in the oil & gas sector made possible by graphene nanotubes
 |
Abstract:
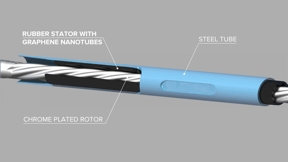
As is well known in the oil industry, one of the most common reasons for drilling tools breaking down is failure of rubber polymer. A leading producer of oil industry equipment in China has found that graphene nanotubes improve abrasion resistance of the rubber stator by 20% and increase tensile modulus by 30%, resulting in a shortened drilling cycle, reduced energy consumption and less environmental pollution from the drilling equipment.
Drilling speed increased by 20% – yet another upgrade in the oil & gas sector made possible by graphene nanotubes
Luxembourg | Posted on January 15th, 201956% of drilling tool failures in the oil extraction industry are caused by low durability of the rubber stator – one of the most important elements in a screw drill. In China, annual losses from the failure of drilling tools are estimated to be more than $40,000 per oil well. Equipment manufacturers are thus always looking for ways to improve the rubber used in screw drilling tools, to reduce these financial losses for oil-extracting companies.
One of the largest Chinese producers of PDM drilling tools, Orient Energy & Technology Ltd., has completed laboratory testing of nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) containing TUBALL graphene nanotubes, produced by OCSiAl. Just 1.7 wt.% of graphene nanotube concentrate introduced into NBR was found to increase the tensile modulus by 30%.
“Improving the modulus of elasticity is the most valuable advantage of graphene nanotubes in our industry, because that leads to a 30% increase in output torque of our products. With that, the drilling speed can also be increased by more than 20%, resulting in a shortened drilling cycle, reduced energy consumption and less environmental pollution, greatly improving China’s drilling technology,” said Mr. Hu, a rubber engineer at Orient Energy & Technology. At the same time, the graphene nanotubes result in a reduction of abrasion by 20% without increasing the Mooney viscosity of rubber, whereas other additives such as multi wall carbon nanotubes increase viscosity, which is unacceptable for injecting.
Graphene nanotubes are one of the allotropic forms of carbon, where each tube can be considered to be a rolled-up sheet of graphene. This universal additive is already on duty protecting the oil & gas industry, where it is widely applied as a conductive additive in fiberglass pipes for permanent and uniform conductivity, as well as 15% reinforcement. Another example is anti-static fiberglass tanks for storing and transporting easily combustible materials, where these nanotubes ensure permanent and stable resistivity of less than 10^6 Ω·cm, without “hot spots” and independent of humidity.
Orient Energy & Technology is continuing to test TUBALL graphene nanotubes, in particular by studying their effects on other types of rubber, such as HNBR and FKM. Meanwhile, the first industrial prototype of a TUBALL-enhanced NBR stator for a screw drill is undergoing industrial trials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anastasia Zirka
PR & Advertising manager
OCSiAl Group
+7 913 989 9239
Copyright © OCSiAl Group
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








