Home > Press > Quantum mechanics work lets oil industry know promise of recovery experiments
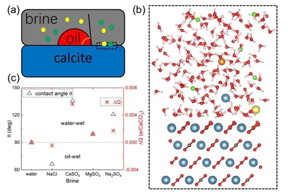 |
| Clockwise from top left: a schematic diagram of the calcite/brine/oil system, a simulation supercell (color scheme: Ca-indigo, C-brown, O-red, H-white) with ions in brine shown schematically, and the oil-in-water contact angle assuming an initial mixed-wet state and difference (relative to calcite-water) in the effective charge of the surface. CREDIT Sokrates Pantelides |
Abstract:
With their current approach, energy companies can extract about 35 percent of the oil in each well. Every 1 percent above that, compounded across thousands of wells, can mean billions of dollars in additional revenue for the companies and supply for consumers.
Quantum mechanics work lets oil industry know promise of recovery experiments
Nashville, TN | Posted on September 28th, 2018Extra oil can be pushed out of wells by forced water - often inexpensive seawater - but scientists doing experiments in the lab found that sodium in water impedes its ability to push oil out, while other trace elements help. Scientists experiment with various combinations of calcium, magnesium, sulfates and other additives, or "wettability modifiers," in the laboratory first, using the same calcite as is present in the well. The goal is to determine which lead to the most oil recovery from the rock.
Vanderbilt University physicist Sokrates Pantelides and postdoctoral fellow in physics Jian Liu developed detailed quantum mechanical simulations on the atomic scale that accurately predict the outcomes of various additive combinations in the water.
They found that calcium, magnesium and sulfates settle farther from the calcite surface, rendering it more water-wet by modifying the effective charge on the surface, enhancing oil recovery. Their predictions have been backed by experiments carried out by their collaborators at Khalifa University in Abu Dhabi: Saeed Alhassan, associate professor of chemical engineering and director of the Gas Research Center, and his research associate, Omar Wani.
"Now, scientists in the lab will have a procedure by which they can make intelligent decisions on experiments instead of just trying different things," said Pantelides, University Distinguished Professor of Physics and Engineering, William A. & Nancy F. McMinn Professor of Physics, and professor of electrical engineering. "The discoveries also set the stage for future work that can optimize choices for candidate ions."
The team's paper, ญญญญญ"Wettability alteration and enhanced oil recovery induced by proximal adsorption of Na+, Cl-, Ca2+, Mg2+, and SO42- ions on calcite," appears today in the journal Physical Review Applied. It builds on Pantelides' previous work on wettability, released earlier this year.
His co-investigators in Abu Dhabi said the work will have a significant impact on the oil industry.
"We are excited to shed light on combining molecular simulations and experimentation in the field of enhanced oil recovery to allow for more concrete conclusions on the main phenomenon governing the process," Alhassan said. "This work showcases a classic approach in materials science and implements it in the oil and gas industry: the combination of modeling and experiment to provide understanding and solutions to underlying problems."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Heidi Nieland Hall
615-322-6614
Copyright © Vanderbilt University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








