Home > Press > Alzheimer's breakthrough: Brain metals that may drive disease progression revealed: In brains affected by Alzheimer's, researchers identify chemically reduced iron species, with mineral forms including a magnetic iron oxide
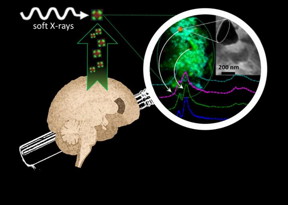 |
| In brains affected by Alzheimer's, researchers identify chemically reduced iron species, with mineral forms including a magnetic iron oxide which they hypothesize are produced during formation of amyloid protein plaques CREDIT University of Warwick/Dr Joanna Collingwood |
Abstract:
•Breakthrough in description of metals in brain which may drive the progression of Alzheimer's disease, made by international research collaboration, including University of Warwick
•In brains affected by Alzheimer's, researchers identify chemically reduced iron species, with mineral forms including a magnetic iron oxide which they hypothesize are produced during formation of amyloid protein plaques
•Understanding the impact and management of these metals could lead to more effective future therapies for Alzheimer's
Alzheimer's breakthrough: Brain metals that may drive disease progression revealed: In brains affected by Alzheimer's, researchers identify chemically reduced iron species, with mineral forms including a magnetic iron oxide
Coventry, UK | Posted on June 22nd, 2018Alzheimer's disease could be better treated, thanks to a breakthrough discovery of the properties of the metals in the brain involved in the progression of the neurodegenerative condition, by an international research collaboration including the University of Warwick.
Dr Joanna Collingwood, from Warwick's School of Engineering, was part of a research team which characterised iron species associated with the formation of amyloid protein plaques in the human brain - abnormal clusters of proteins in the brain. The formation of these plaques is associated with toxicity which causes cell and tissue death, leading to mental deterioration in Alzheimer's patients.
They found that in brains affected by Alzheimer's, several chemically-reduced iron species including a proliferation of a magnetic iron oxide called magnetite - which is not commonly found in the human brain - occur in the amyloid protein plaques. The team had previously shown that these minerals can form when iron and the amyloid protein interact with each other. Thanks to advanced measurement capabilities at synchrotron X-ray facilities in the UK and USA, including the Diamond Light Source I08 beamline in Oxfordshire, the team has now shown detailed evidence that these processes took place in the brains of individuals who had Alzheimer's disease. They also made unique observations about the forms of calcium minerals present in the amyloid plaques.
Understanding the significance of these metals to the progression of Alzheimer's could lead to more effective future therapies which combat the disease at its root.
Dr Joanna Collingwood, Associate Professor at the University of Warwick's School of Engineering and expert in trace metals analysis, high resolution imaging, and neurodegenerative disorders, commented:
"Iron is an essential element in the brain, so it is critical to understand how its management is affected in Alzheimer's disease. The advanced X-ray techniques that we used in this study have delivered a step-change in the level of information that we can obtain about iron chemistry in the amyloid plaques. We are excited to have these new insights into how amyloid plaque formation influences iron chemistry in the human brain, as our findings coincide with efforts by others to treat Alzheimer's disease with iron-modifying drugs."
The team, led by an EPSRC-funded collaboration between University of Warwick and Keele University - and which includes researchers from University of Florida and The University of Texas at San Antonio - made their discovery by extracting amyloid plaque cores from two deceased patients who had a formal diagnosis of Alzheimer's.
The researchers scanned the plaque cores using state-of-the-art X-ray microscopy at the Advanced Light Source in Berkeley, USA and at beamline I08 at the Diamond Light Source synchrotron in Oxfordshire, to determine the chemical properties of the minerals within them.
They also analysed the magnetic state of the iron species in the plaques to confirm the presence of various iron minerals including the magnetic iron oxide magnetite.
The research team propose that interactions between iron and amyloid that produce the chemically reduced iron species, including magnetite, may account for toxicity that contributes to the development and progression of Alzheimer's.
There are 850,000 people with dementia in the UK, with numbers set to rise to over 1 million by 2025. This will soar to 2 million by 2051.
There is no cure for Alzheimer's disease or any other type of dementia. Delaying the onset of dementia by five years would halve the number of deaths from the condition, saving 30,000 lives a year.
###
It is authored by James Everett, Joanna F. Collingwood, Vindy Tjendana-Tjhin, Jake Brooks, Frederik Lermyte, Germán Plascencia-Villa, Ian Hands-Portman, Jon Dobson, George Perry and Neil D. Telling.
This work was supported by EPSRC grants EP/K035193/1 (JFC), EP/N033191/1-EP/N033140/1 (JFC-NDT), the Alzheimer's Association (AARFD-17-529742), University of Warwick alumni donations (VTT, JE), the RCMI Program from NIH at UTSA (5G12RR013646, G12MD007591), San Antonio Life Sciences Institute (SALSI)-Clusters in Research Excellence Program, and Semmes Foundation.
####
About University of Warwick
The University of Warwick's School of Engineering is one of the leading unified engineering schools in the UK. The department's research was ranked third in the Research Excellence Framework 2014 for General Engineering.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Tom Frew
Copyright © University of Warwick
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








