Home > Press > Squeezing light at the nanoscale: Ultra-confined light could detect harmful molecules
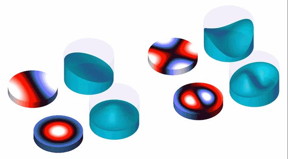 |
| Nano-discs act as micro-resonators, trapping infrared photons and generating polaritons. When illuminated with infrared light, the discs concentrate light in a volume thousands of times smaller than is possible with standard optical materials. At such high concentrations, the polaritons oscillate like water sloshing in a glass, changing their oscillation depending on the frequency of the incident light. CREDIT Harvard SEAS |
Abstract:
Researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed a new technique to squeeze infrared light into ultra-confined spaces, generating an intense, nanoscale antenna that could be used to detect single biomolecules.
Squeezing light at the nanoscale: Ultra-confined light could detect harmful molecules
Cambridge, MA | Posted on June 17th, 2018The researchers harnessed the power of polaritons, particles that blur the distinction between light and matter. This ultra-confined light can be used to detect very small amounts of matter close to the polaritons. For example, many hazardous substances, such as formaldehyde, have an infrared signature that can be magnified by these antennas. The shape and size of the polaritons can also be tuned, paving the way to smart infrared detectors and biosensors.
The research is published in Science Advances.
"This work opens up a new frontier in nanophotonics," said Federico Capasso, the Robert L. Wallace Professor of Applied Physics and Vinton Hayes Senior Research Fellow in Electrical Engineering, and senior author of the study. "By coupling light to atomic vibrations, we have concentrated light into nanodevices much smaller than its wavelength, giving us a new tool to detect and manipulate molecules."
Polaritons are hybrid quantum mechanical particles, made up of a photon strongly coupled to vibrating atoms in a two-dimensional crystal.
"Our goal was to harness this strong interaction between light and matter and engineer polaritons to focus light in very small spaces," said Michele Tamagnone, postdoctoral fellow in Applied Physics at SEAS and co-first author of the paper.
The researchers built nano-discs -- the smallest about 50 nanometers high and 200 nanometers wide -- made of two-dimensional boron nitride crystals. These materials act as micro-resonators, trapping infrared photons and generating polaritons. When illuminated with infrared light, the discs were able to concentrate light in a volume thousands of times smaller than is possible with standard optical materials, such as glass.
At such high concentrations, the researchers noticed something curious about the behavior of the polaritons: they oscillated like water sloshing in a glass, changing their oscillation depending on the frequency of the incident light.
"If you tip a cup back-and-forth, the water in the glass oscillates in one direction. If you swirl your cup, the water inside the glass oscillates in another direction. The polaritons oscillate in a similar way, as if the nano-discs are to light what a cup is to water," said Tamagnone.
Unlike traditional optical materials, these boron nitride crystals are not limited in size by the wavelength of light, meaning there is no limit to how small the cup can be. These materials also have tiny optical losses, meaning that light confined to the disc can oscillate for a long time before it settles, making the light inside even more intense.
The researchers further concentrated light by placing two discs with matching oscillations next to each other, trapping light in the 50-nanometer gap between them and creating an infrared antenna. As light concentrates in smaller and smaller volumes, its intensity increases, creating optical fields so strong they can exert measurable force on nearby particles.
"These light-induced forces serve also as one our detection mechanisms," said Antonio Ambrosio, a principal scientist at Harvard's Center for Nanoscale Systems. "We observed this ultra-confined light by the motion it induces on an atomically sharp tip connected to a cantilever."
A future challenge for the Harvard team is to optimize these light nano-concentrators to achieve intensities high enough to enhance the interaction with a single molecule to detectable values.
###
This research was co-authored by Kundan Chaudhary, Luis A. Jauregui, Philip Kim and William L. Wilson. It was supported by the National Science Foundation and the Swiss National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Leah Burrows
617-496-1351
Copyright © Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
![]() Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








