Home > Press > A micro-thermometer to record tiny temperature changes
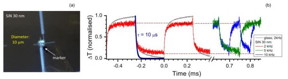 |
| (a) Video still showing a tightly focused laser beam making contact with the thermocouple. (b) Graph showing the thermocouple's response over time to different laser powers (3.6 and 1.8 mW) at different repetition rates, on glass and on the silicon nitride membrane (ΔT: change in temperature, τ: time for temperature rise and decay). CREDIT Scientific Reports |
Abstract:
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) and their collaborators have developed a micrometer-wide thermometer that is sensitive to heat generated by optical and electron beams, and can measure small and rapid temperature changes in real time. This new device can be used to explore heat transport on the micro- and nano-scales, and in optical microscopy and synchrotron radiation experiments.
A micro-thermometer to record tiny temperature changes
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on May 15th, 2018There is an urgent need for a device that can measure thermal behavior on the nanoscale and in real time, as this technology could be applied in photo-thermal cancer treatment as well as in advanced research on crystals, optical light harvesting, etc. Moreover, a miniaturized thermal microscopy system with a nanoscale heat source and detector is essential for future development of next-generation transistors that will be employed in designing new nanoscale devices.
A thermocouple is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming electrical junctions at differing temperatures. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage, which can be interpreted to measure temperature. The micro-thermocouple recently developed by scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology and their collaborators is of major importance to researchers in many fields. This device consists of a gold and nickel thermocouple on a silicon nitride membrane and is miniaturized to the extent that the electrodes are only 2.5 μm wide and the membrane is just 30 nm thick. For such a system to be used as a thermal characterization device, i.e., a thermometer, it must show sensitivity to temperature change. The developed micro-thermocouple exhibited high responsiveness to heat generated by a laser and an electron beam. Importantly, tiny temperature changes were measured by the developed thermocouple for both types of heating.
An already developed miniaturization process was used to prepare the micro-thermocouple, but critical improvements were made. In the established method, a cross pattern of metal stripes with widths of a few micrometers is created, so that a thermocouple is produced. The researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology and their colleagues used this technique to create a pattern on a nano-thin silicon nitride membrane, which enhanced the device sensitivity and enabled it to respond faster. Through this approach, a thermometer that could measure fast and small temperature changes was successfully produced, with the measurements being performed through the nano-thin silicon nitride membrane.
As explained above, both a nanoscale heat source and a nanoscale detector are needed for a miniaturized thermal microscopy system. These requirements were successfully satisfied by the researchers, who used the nano-thin membrane and a tightly focused laser or electron beam to create a heat source with a diameter of less than 1 μm. So, combined with the micro-thermocouple detector, a nanoscale thermal microscopy system was achieved. This system can be regarded as a new "toolbox" for investigating heat transport behavior on the micro- and nano-scales, with many important applications in a wide range of fields.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Emiko Kawaguchi
81-357-342-975
Copyright © Tokyo Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








