Home > Press > Elastic microspheres expand understanding of embryonic development and cancer cells
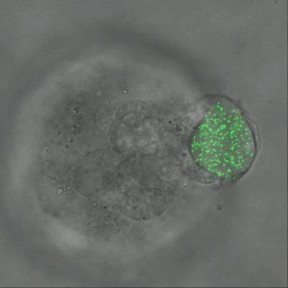 |
| Twenty-four hour time-elapsed video shows melanoma tumor cells of mice squeezing and rotating an elastic microgel sphere filled with fluorescent nanoparticles. CREDIT Video courtesy Ning Wang. |
Abstract:
A new technique that uses tiny elastic balls filled with fluorescent nanoparticles aims to expand the understanding of the mechanical forces that exist between cells, researchers report. A University of Illinois-led team has demonstrated the quantification of 3-D forces within cells living in petri dishes as well as live specimens. This research may unlock some of the mysteries related to embryonic development and cancer stem cells, i.e., tumor-repopulating cells.
Elastic microspheres expand understanding of embryonic development and cancer cells
Champaign, IL | Posted on May 15th, 2018For decades, scientists have struggled to quantify the forces, called tractions, that push, pull and squeeze cells throughout their lifecycles. The tools available to measure force were not small enough to fit into intercellular spaces or sensitive enough to detect the miniscule movements within cell colonies.
Although small on a human scale, the magnitudes of these mechanical forces are far from trivial at the cellular level. According to the new study, prior research by the Illinois group and others indicates that traction plays a fundamental role in cell physiology.
The team led by mechanical science and engineering professor Ning Wang reported their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
"If we place a single cell in a medium within a petri dish it will not survive for long, even if we provide all of the nutrients needed," Wang said. "The cells fail to form any sort of tissue because there is no support or scaffolding on which to build."
As cells grow and reproduce, they exert forces on each other while competing for space. The team found that if they inject their tiny elastic spheres into early stage embryos of zebrafish and colonies of melanoma cells of mice in petri dishes, they too experience the forces.
"The cells do not seem to mind the intrusion," Wang said. "The spheres are made of a nontoxic microgel and even though the cells will push them around, they do not seem to interfere with development."
To measure the amount of force imposed on the cells, the team placed fluorescent nanoparticles inside of the spheres. When the cells squeeze the spheres, the nanoparticles all move the same amount per area of force. The researchers can then measure the motions of the glowing particles using fluorescent light microscopy to calculate the amount of force exerted on the spheres and cells. Using this technique, the team has marked the first successful measurement of all three types of force - compression, tension and shear - in all three dimensions, Wang said.
This ability to quantify force in cells may be very important to cancer cell research, Wang said. The team found that when melanoma tumor cells of mice in vitro begin to reproduce from a single cell to about 100 to 200 cells, compressive stress does not increase.
"We thought that cancer cells would generate more pressure at this early growth stage while the mass of the tumor increases, as we observed in zebrafish embryos, but they do not," Wang said. "We suspect that the cancer cells begin to spread out or metastasize right after this stage."
Primary tumors are usually not deadly, Wang said. The real killer appears to be the spread of tumor-repopulating cells from primary tumors into soft tissues - with low intercellular tractions - like bone marrow, brain, lung and liver. "Although the underlying mechanism for metastasis is unclear, we have hypothesized that tumor-repopulating cells spread very rapidly in these secondary soft tissues. Having the ability to measure changes in tractions at the intercellular level may serve as an early cancer-detection tool," Wang said.
This microgel sphere technology may also help unravel the mechanisms behind a metastasis-halting synthetic drug recently described by Wang and his colleagues. In addition, Wang's co-authors are continuing to apply this technology to stem and embryonic cell research. "When other researchers see this powerful new tool that we have developed, they will be excited to use it in many different cell physiology, development and disease applications," Wang said.
###
The National Institutes of Health supported this study.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lois E Yoksoulian
217-244-2788
Ning Wang
217-265-0913
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








