Home > Press > Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping: Cell-to-cell variation in gene expression creates a need for techniques that can characterize expression at the level of individual cells
 |
| University of Toronto researchers developed a liquid biopsy technology to improve prostate cancer treatment. CREDIT University of Toronto |
Abstract:
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men and the fifth leading cause of death from cancer in men worldwide, according to 2012 numbers. While several viable treatment options for prostate cancer exist, many men affected with prostate cancer will not respond to first-line treatments. Researchers in the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences at the Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Toronto have developed a new technology for liquid biopsy to identify which patients may not respond to standard therapy before it is delivered.
Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping: Cell-to-cell variation in gene expression creates a need for techniques that can characterize expression at the level of individual cells
Toronto, Canada | Posted on April 2nd, 2018"Screening for drug resistance is key to improving treatment approaches for many cancers," said Shana Kelley, scientist and professor at the Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Toronto. "It's important for patients not to be on a therapy that won't help them and it's also important for healthcare systems to avoid, whenever possible, delivering ineffective treatments."
The ability to screen patients using a blood sample as opposed to more invasive techniques required for conventional biopsies is also a step forward.
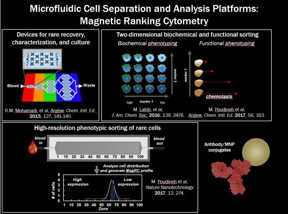
Kelley, lead investigator on the study published today in Nature Chemistry, explained how her team has advanced a completely new approach using magnetic nanoparticles with DNA capture probes on their surface that can target circulating tumour cells (CTCs) in blood samples to see if the cells contains biomarkers associated with drug resistance. "We can then trap the individual magnetized cells in a microfluidic device built in the lab, isolating them from all the other cells in the sample and allowing us to perform highly sensitive analysis," Kelley said. The cells with the highest magnetic content will also have high mRNA expression for the biomarker associated with drug resistance.
"This means that patients with high mRNA expression should be considered for other therapies because they won't respond to the first-line treatment."
Targeting CTCs, the cells responsible for spreading cancer, is important because they carry information from the primary tumour that can inform treatment; however, they are outnumbered by a billion-to-one by normal cells in a patient' blood and are therefore extremely challenging to capture. In 2016, Kelley and her team published a study in Nature Nanotechnology that first introduced the microfluidic device and how it could be used to trap and analyze CTCs. The current study builds on this previous work by further targeting a specific biomarker within the CTCs.
The blood samples analyzed were collected from a small cohort of patients undergoing treatment for metastatic prostate cancer. In 10 of the patients tested, CTCs were visualized but only four of the patients exhibited the biomarker associated with drug resistance. This finding demonstrates that the new method can provide both a CTC count and an analysis of the clinically relevant biomarker.
"We are very excited because this is like finding a needle in a haystack. It paves the way for a straightforward and personalized screening tool that allows clinicians to see if a patient will respond to therapy or not. Our method is also rapid, accurate and inexpensive, which gives it real potential for clinical uptake," said Kelley.
As for next steps, the finding must be replicated in a larger study, Kelley explained. Her team is also focused on "scaling up" and expanding the application of this technology to other forms of cancer and other diseases.
"Liquid biopsy is one of the most promising tools emerging for the management of cancer," said Kelley "and we are excited about the potential of our technology to streamline this type of testing."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kate Richards
416-978-7117
Copyright © University of Toronto
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








