Home > Press > Superconductivity in an alloy with quasicrystal structure
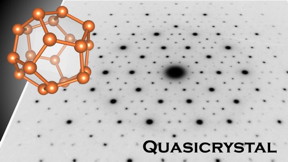 |
| An electron diffraction pattern of Al-Zn-Mg quasicrystal with a dodecahedron forming a Bergman-type cluster. CREDIT Keiichiro Imura, Noriaki K. Sato, and Tsutomu Ishimasa |
Abstract:
Extraordinary things happen at low temperatures. One of the best examples is surely superconductivity. This phenomenon, wherein the electrical resistance of a solid drops to zero below a critical temperature, has been known for a century, and now has applications in science and industry. Physics and chemistry students can even make their own levitating magnets from superconducting alloys.
Superconductivity in an alloy with quasicrystal structure
Nagoya, Japan | Posted on March 27th, 2018Most superconductors, like most solids, are crystalline: their atomic structures are built from periodically repeating cells. Since the 1980s an alternative form of solid, the quasicrystal (QC), has become prominent. Although QCs have symmetry, like crystals, they have no repeat units. This lack of periodicity results in unusual electronic structures. Now, in a study in Nature Communications, a research team led by Nagoya University has discovered superconductivity in a QC for the first time.
The team studied an alloy of aluminum, zinc and magnesium. The crystalline version is known to be superconducting. However, the structure of Al-Zn-Mg depends on the ratio of the three elements. The team found that Al had a crucial effect on the alloy's properties. As study first author Keisuke Kamiya notes, "When we reduced the Al content while keeping the Mg content almost constant, the critical temperature for superconductivity at first decreased gradually from ~0.8 to ~0.2 K. However, at 15% Al, two things happened: the alloy transformed into a quasicrystal, and the critical temperature plummeted to ~0.05 K."
This extremely low critical temperature, just 1/20 of a degree above absolute zero, explains why superconductivity in QCs has proven so hard to achieve. Nonetheless, the QC alloy showed two archetypal features of superconductors: a jump in specific heat at the critical temperature, and the almost total exclusion of magnetic flux from the interior, known as the Meissner effect.
Superconduction in conventional crystals is now well-understood. At sufficiently low temperature, the negatively charged electrons overcome their mutual repulsion and attract one another, teaming up into pairs. These "Cooper pairs" coalesce into a Bose-Einstein condensate, a quantum state of matter with zero electrical resistance. However, the attraction between electrons relies on their interaction with the solid lattice, and conventional theory assumes this is a periodic crystal, rather than a QC.
For the origin of superconduction in the QC alloy, the team considered three possibilities. The most exotic was "critical eigenstates": special electronic states only found near absolute zero. The electronic eigenstates are extended in crystals, and localized in random solids, but the spatial extent of the critical eigenstates in QCs--which are neither periodic nor random--is unclear. However, the team ruled them out based on their measurements. That led back to Cooper pairs, in either the extended or the less-common "weak-coupling" variety. In fact, the alloy closely resembled a typical weak-coupling superconductor.
"It's interesting that the superconductivity of this alloy was not linked to its quasicrystallinity, but resembled that in so-called dirty crystals," says corresponding author Noriaki K. Sato. "However, the theory of quasicrystals also predicts another form of superconduction, based on fractal geometry in QCs. We believe there is a strong possibility that fractal superconductivity makes at least some contribution, and we would be excited to finally measure it."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Koomi Sung
Copyright © Nagoya University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








