Home > Press > Histology in 3-D: New staining method enables Nano-CT imaging of tissue samples
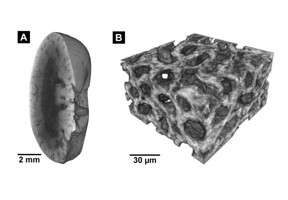 |
| These images were created using the new staining method: left: Micro-CT image of a mouse kidney, right: Nano-CT image of the same tissue. CREDIT Mueller, Pfeiffer / TUM / reproduced with permission from PNAS. |
Abstract:
To date, examining patient tissue samples has meant cutting them into thin slices for histological analysis. This might now be set to change - thanks to a new staining method devised by an interdisciplinary team from the Technical University of Munich (TUM). This allows specialists to investigate three-dimensional tissue samples using the Nano-CT system also recently developed at TUM.
Histology in 3-D: New staining method enables Nano-CT imaging of tissue samples
Munich, Germany | Posted on February 22nd, 2018Tissue sectioning is a routine procedure in hospitals, for instance to investigate tumors. As the name implies, it entails cutting samples of body tissue into thin slices, then staining them and examining them under a microscope. Medical professionals have long dreamt of the possibility of examining the entire, three-dimensional tissue sample and not just the individual slices. The most obvious way forward here lies in computed tomography (CT) scanning - also a standard method used in everyday clinical workflows.
Previous limitations in resolution and contrast
Thus far, there have been two major hurdles to the realization of this goal. Firstly, the resolution of conventional CT scanners is too low. Today's Micro- and Nano-CT systems are rarely suitable for use in frontline medicine. Some do not offer sufficiently high resolution, while others rely on radiation from large particle accelerators.
Secondly, soft tissue is notoriously difficult to examine using CT equipment. Samples have to be stained to render them visible in the first place. Stains for CT scanning are sometimes highly toxic, and they are also extremely time-consuming to apply. At times they modify the tissue to such an extent that further analysis is then impossible.
Successful collaboration between physics, chemistry and medicine
Now, however, scientists at TUM's Munich School of BioEngineering (MSB) have solved both problems. In November 2017, Prof. Franz Pfeiffer and his team unveiled a Nano-CT system that delivers resolutions of up to 100 nanometers and is suitable for use in typical laboratory settings. In the current issue of the scientific journal PNAS, the cross-disciplinary research team from physics, chemistry and medicine also presents a staining method for histological examination with Nano-CT.
Compatibility with conventional methods
Using a mouse kidney, the scientists have successfully demonstrated that Nano-CT is able to generate 3D images that match the information granularity of tissue sections. At the core of the staining method lies eosin, a standard dye used in tissue sampling that was previously considered unsuitable for CT.
"Our approach included developing a special pre-treatment so that we can use eosin anyway," outlines chemist Dr. Madleen Busse. The staining method is so time-efficient that it is also suited to everyday clinical workflows. "Another important benefit is that there are no problems using established methods to examine the tissue sample following the scan," adds Busse.
Enhancement rather than replacement
In the next step, the researchers are looking to examine human tissue samples. However, CT histology is not set to replace conventional methods any time soon. For the moment, at least, the team views the new procedure as supplementary - for instance giving doctors additional insights into the three-dimensional distribution of cells and nuclei. Franz Pfeiffer also sees new opportunities here for basic medical research: "Alongside diagnostic applications, the non-destructive 3D examination enabled by Nano-CT could deliver new insights into the microscopic origins of widespread diseases such as cancer."
####
About Technical University of Munich (TUM)
The Nano-CT system and staining method were developed at the Munich School of BioEngineering (MSB) This interdisciplinary TUM research center is Europe's most multi-disciplinary university institution focused on the interface between medicine, engineering and natural sciences. Franz Pfeiffer, Professor of Biomedical Physics is Director of the MSB.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Paul Hellmich
49-892-892-2731
Prof. Dr. Franz Pfeiffer
Chair of Biomedical Physics and Munich School of BioEngineering
Technical University of Munich
Tel.: 49-89-289-12551
Copyright © Technical University of Munich (TUM)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Munich School of BioEngineering:
Munich School of BioEngineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








